HomeRobotic Database - Robotic platform | TERRINet
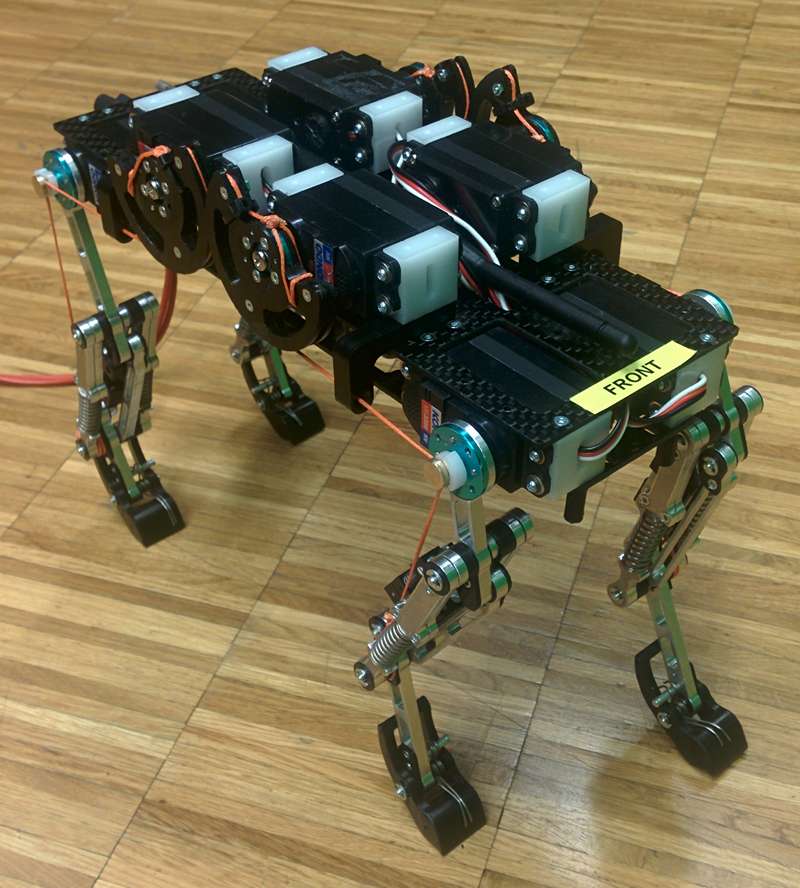

Cheetah-Cub-AL
Cheetah-Cub (https://biorob.epfl.ch/cheetah) was not fundamentally altered from its early development days. Some major changes are introduced with Cheetah-Cub-AL. The leg was redesigned and features now a (to the saggital plane of the leg) symmetric diagonal spring, canceling unwanted bending behavior present in previous Cheetah-Cub-versions. Additionally, making use of classical CNC manufacturing techniques with aluminum in combination with ball-bearings in every joint, friction was reduced, alignment of the axis and repeatability of experiments were improved. The changes to the trunk are little but feature now an easy access to the control board for development purposes. Another major change is the switch to a new operating system, Jokto, that improves stability and ease of use. Tuleu implemented inverse-kinematics of the legs for control purposes. This allowed to tune gaits much faster andmore intuitively. The robot was featured recently in Prof. Ijspeert’s talk in TED Global Geneva.
Key features:
- It is lightweight, compact, electrically powered
- It shows self-stabilizing behavior over a large range of speeds with open loop control
- It is cheap, easy to reproduce, robust, and safe to handle
Possible applications:
- Exploring different neural networks inspired by animals as high-level controllers
- Platform as light sensor carrier, such as a small camera
- Animal gait exploration
- Researching different feet or legs designs
- Search and rescue
Technical specifications
| RC servo motor: | Kondo KRS2350 ICS (8x) |
| dhip-shoulder: | 0.206m |
| dshoulder-shoulder: | 0.1m |
| lhip, standing height: | 0.164m |
| Mactuators, sum: | 590g |
| Mrobot: | 1200g |
| Active degrees of freedom: | 8 |
| Gait type: | Trot |
| Body lengths per second: | 3.88 |
| Froude number FR (v^2/G/lhip): | 0.4 |
| Maximum speed, vmax: | 0.8 m/s |
| Stall torque RC servo: | 2Nm at 6V |
| Speed max RC servo: | 0.16s / 60deg at 6V |
| Control board: | RoBoard RB110 |
| Power supply, tethered: | 9V to 11V |
Access information
| Corresponding infrastructure | École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne BioRobotics Lab |
| Location | Route Cantonale, |
| Unit of access | Working day |