HomeRobotic Database - All platforms | TERRINet
Several models of flying robots, as quadrotors and hexarotors aerial robots, in a delimited flight arena of 6mx4mx5m (l,w,h) enclosed by a protective net. The ground is covered by protective mattresses. The arena is equipped with a motion capture system. ARMAR-6 is a collaborative humanoid robot assistant for industrial environments. Designed to recognize the need of help and to allow for an easy and safe human-robot interaction, the robot’s comprehensive sensor setup includes various camera systems, torque sensors and systems for speech recognition. The dual arm system combines human-like kinematics with a payload of 10 kg which allows for dexterous and high-performant dual arm manipulation. In combination with its telescopic torso joint and a pair of underactuated five-finger hands, ARMAR-6 is able to grasp objects on the floor as well as to work in a height of 240 cm. The mobile platform includes holonomic wheels, battery packs and four high-end PCs for autonomous on-board data processing. The Cobomanip assists the operator during handling operation. It is designed as a standard a force generator more than a robot driven in position control mode. In the entire workspace it will assist or oppose to the movements of the operator according to the task definition and the requested assistances. One may therefore consider two distinct operating modes: Movements in free space: the Cobomanip is a perfect balance with 3 or 4 dofs. It behaves like if the load is handled in a zero-gravity area. Constrained movements: motors (one for each dof) apply counteracting torques to limit the manipulator movements into specific directions. All the frictions are compensated with motors situated in the frame of the cobot. COBOMANIP provides assistances to keep the attention of the operator focused on the main task using virtual guides to constrain the movement within a specific part of the workspace. Concepts for such constraints applied to teleoperation tasks are proposed in two distinct types: The operator cannot enter a specific area of the workspace. The movement is possible until a boundary is reached. Assistance to guide the operator. Movements of the operator are limited to those allowed by a mechanism attached to the robot. Intrinsic robotic hand with all functional components (5 motors, tactile sensors and control electronics) integrated in the palm and in the underactuated, self-adaptive fingers. Able to perform multiple grasps and sense objects. Simple communication interface (RS-232 over USB or Bluetooth). Standard prosthetic wrist attachments available (compatible with Ottobock QWD).
The compact size of these hands allows using them in research, evaluation and clinical experience with humans in real daily living environments on human-machine interfaces (either invasive or non-invasive) and control (EMG, ENG, EEG, sensory feedback systems, etc). Not only! Due to their light weight and anthropomorphism they are suitable as robotic end-effectors on limited pay-load robotic arms. Thanks to its unique mechanical qualities, the SYBOT brings competitiveness and attractiveness to manual operations that cannot be automated. Without special training, the operator integrates and optimizes the use of the COBOT by enhancing his know-how in a work environment that does not require any modification. Extremely versatile and portable, the KINOVA Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot is built for human-robot interaction. Which means it’s not intended to automate tasks, but rather to work with people, enabling you to transcend your physical limitations with confidence. The new interface allows simple connectivity with a wide variety of end effectors, instruments and sensors, and the practical controller makes the robot adaptable for multiple application needs. This laboratory is equipped with a state of the art multi-camera motion capture system, various devices for virtual reality immersion, and sporting equipment, ideal for testing wearable robots, body sensor networks and life assistance robots. User studies in a virtual or real environment can be coupled with an EEG measurement system and motion capture in an open space environment. The Robot Companion is a demonstrator of intelligent interactive robotics focusing on industrial assembly tasks (for example the assembly of a representative gear unit). The system is composed of two collaborative robots, custom end-effectors, vision sensors, and a digital twin of the whole platform. In nominal mode, the robots work autonomously and assemble the different parts using dedicated skills. An interactive mode is also available, allowing a human operator to collaborate with the robots. An environment camera allows monitoring the operator’s actions and adapt accordingly. The iCub is a humanoid robot designed to support research in embodied AI. At 104 cm tall, the iCub has the size of a five year old child. It can crawl on all fours, walk and sit up to manipulate objects. Its hands have been designed to support sophisticate manipulation skills. The iCub is distributed as Open Source following the GPL licenses. The entire design is available for download from the project’s repositories (http://www.iCub.org). Four robots are available in the iCub Facility at the Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia. The iCub is one of the few platforms in the world with a sensitive full-body skin to deal with the physical interaction with the environment including possibly people.DIVERSITY IN ALL PARTSDiscover all the
Robotic PlatformsSee here all the Robotic Platforms of our Infrastructures!
Image
Platform
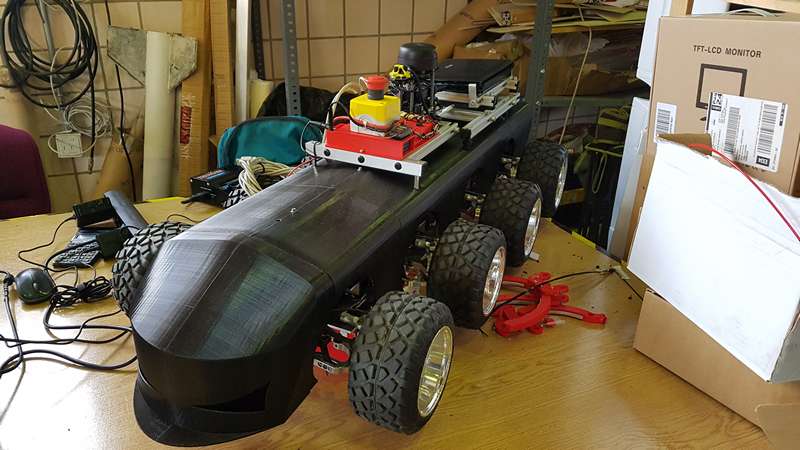

8×8 AGV
Universidad de Sevilla (USE)
Robotics, Vision and Control Group
8×8 AGV
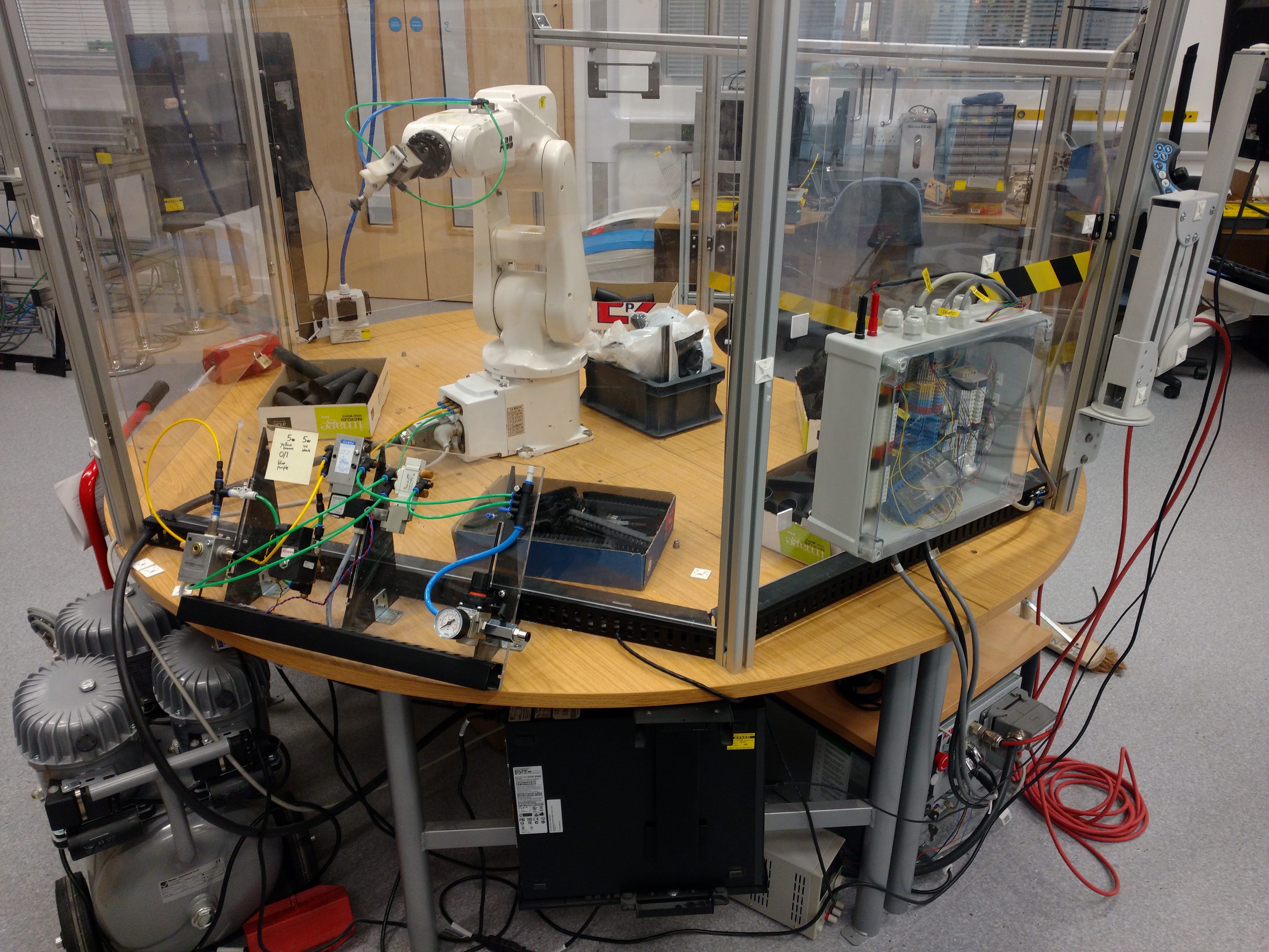
ABB IRB 120
University of the West of England (UWE Bristol)
Bristol Robotics Laboratory
ABB IRB 120
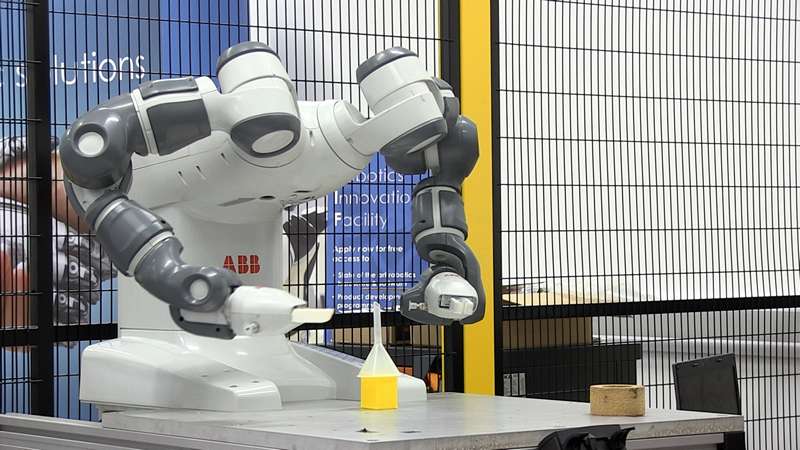

ABB IRB 14000 YuMi
University of the West of England (UWE Bristol)
Robotics Innovation Facility
ABB IRB 14000 YuMi
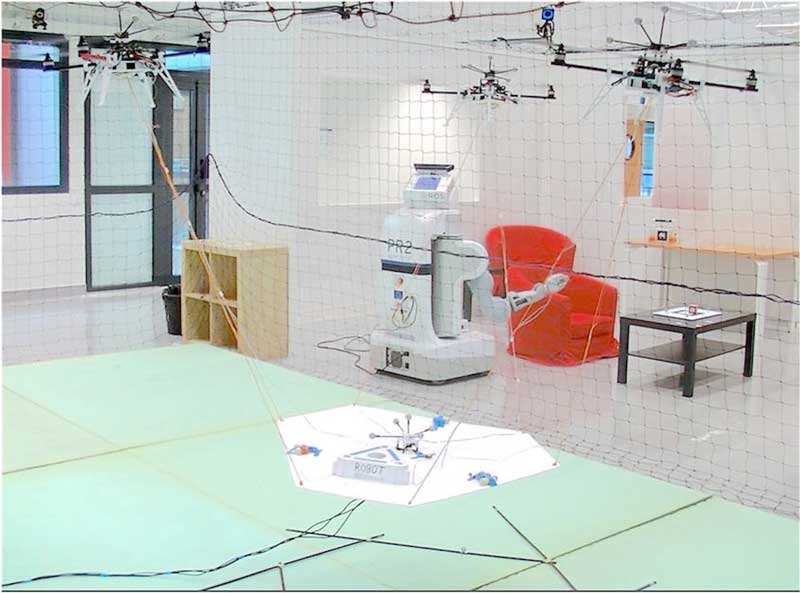

Aerial Robots in a flight arena
Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS)
The Department of Robotics of LAAS
Aerial Robots in a flight arena
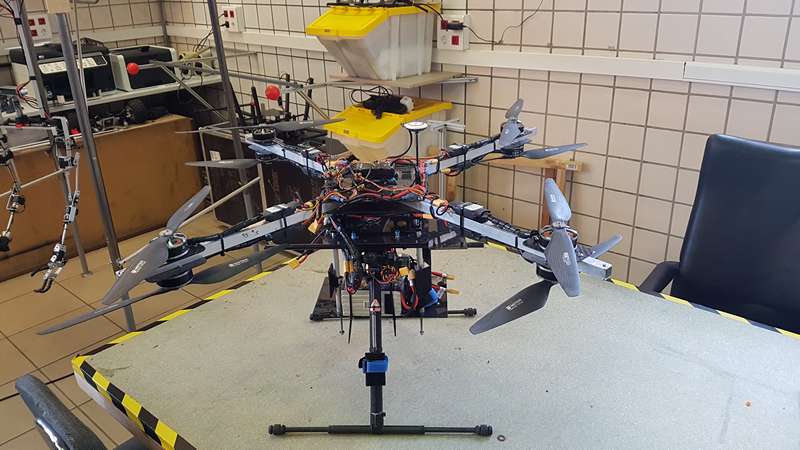

AMUSE
Universidad de Sevilla (USE)
Robotics, Vision and Control Group
AMUSE

Ana and Helena Pioneer robots
Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC)
IRI
Ana and Helena Pioneer robots

AR drone
École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL)
Laboratory of Intelligent Systems
AR drone
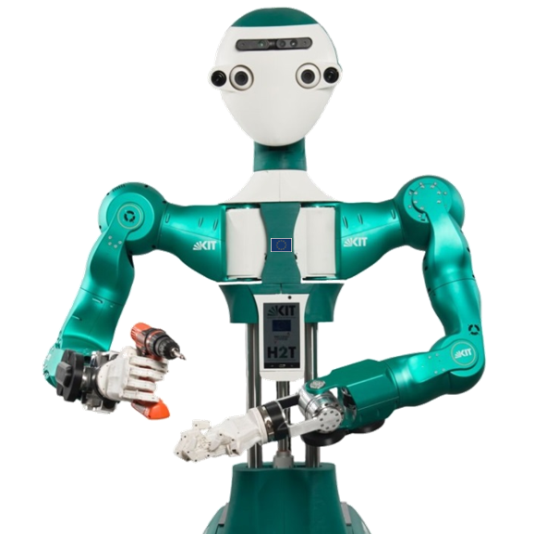

ARMAR 6
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT)
Institute of Anthropomatics and Robotics – High Performance Humanoid Technologies Lab (IAR H2T)
ARMAR 6
The software architecture is implemented in ArmarX (https://armarx.humanoids.kit.edu). High-level functionality, like object localization, navigation, grasping and planning are already implemented and available.
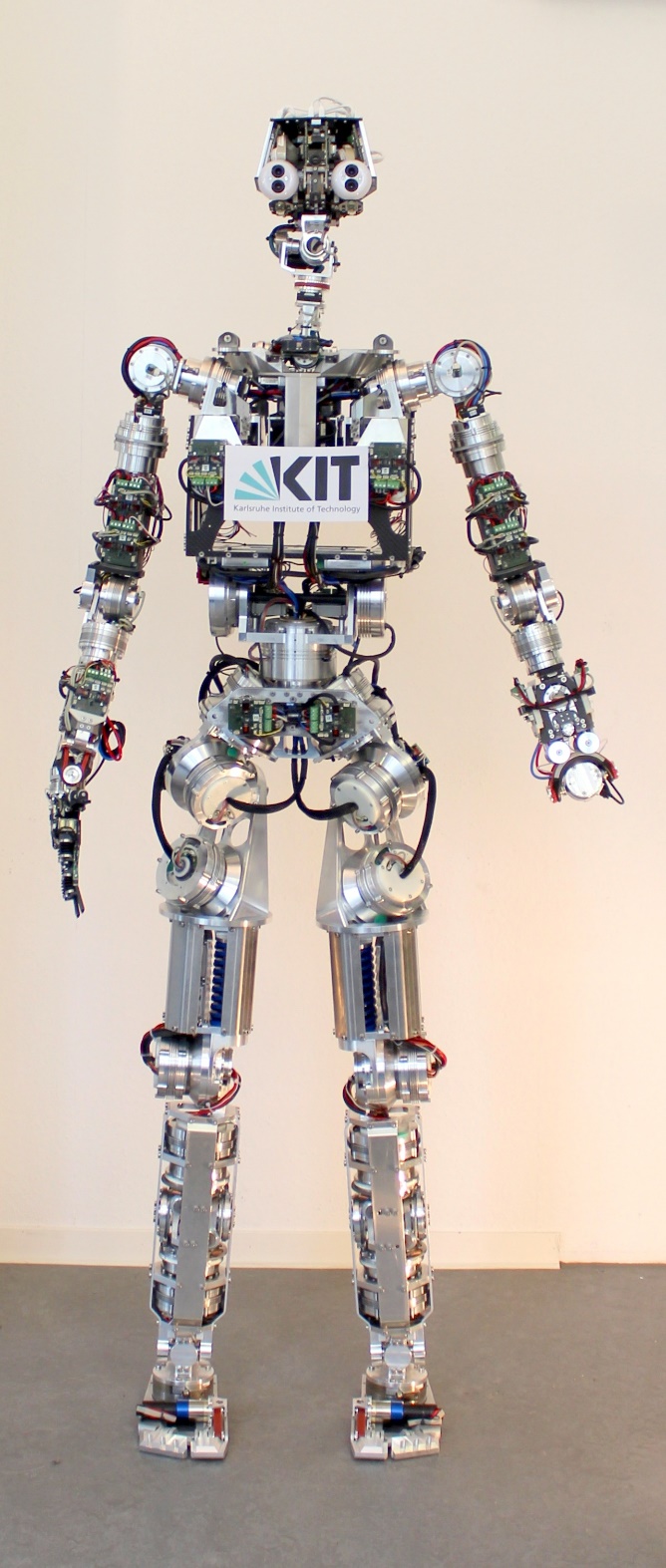

ARMAR-4
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT)
Institute of Anthropomatics and Robotics – High Performance Humanoid Technologies Lab (IAR H2T)
ARMAR-4

ARMAR-III in a robot kitchen
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT)
Institute of Anthropomatics and Robotics – High Performance Humanoid Technologies Lab (IAR H2T)
ARMAR-III in a robot kitchen
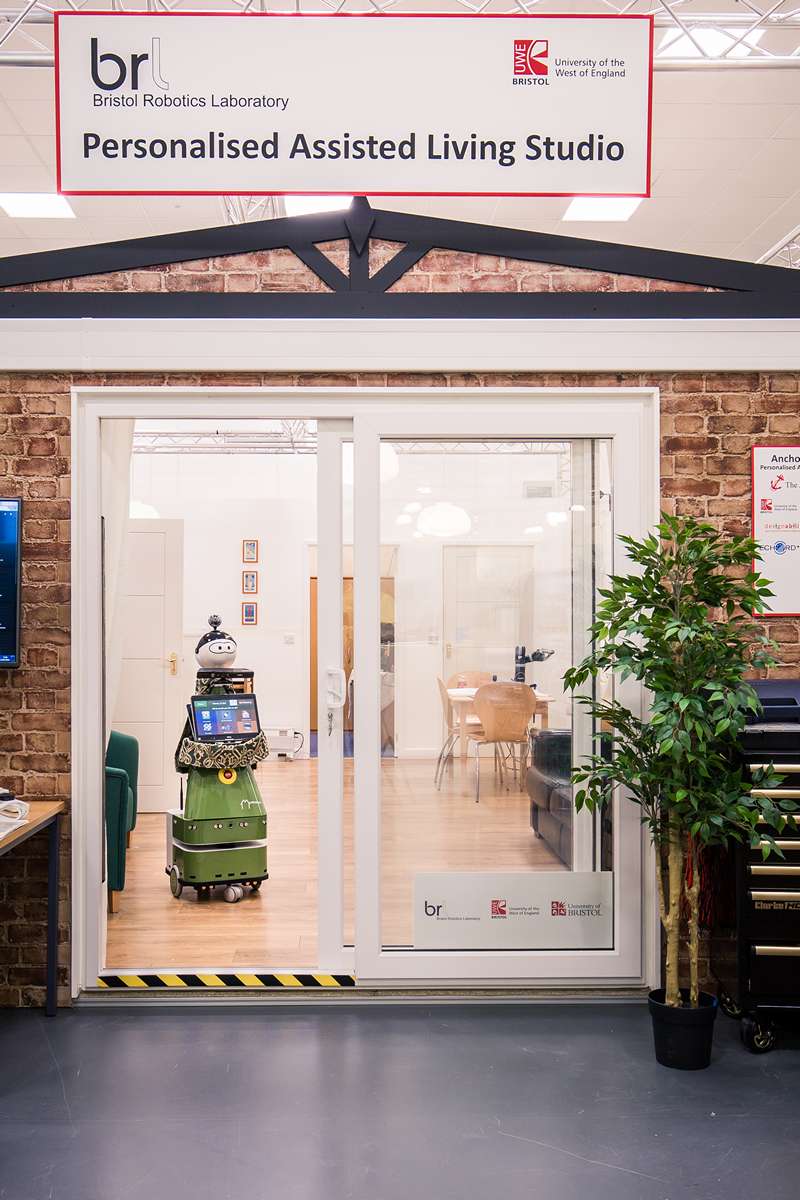

Assisted Living Studio
University of the West of England (UWE Bristol)
Ambient Assisted Living Laboratory
Assisted Living Studio
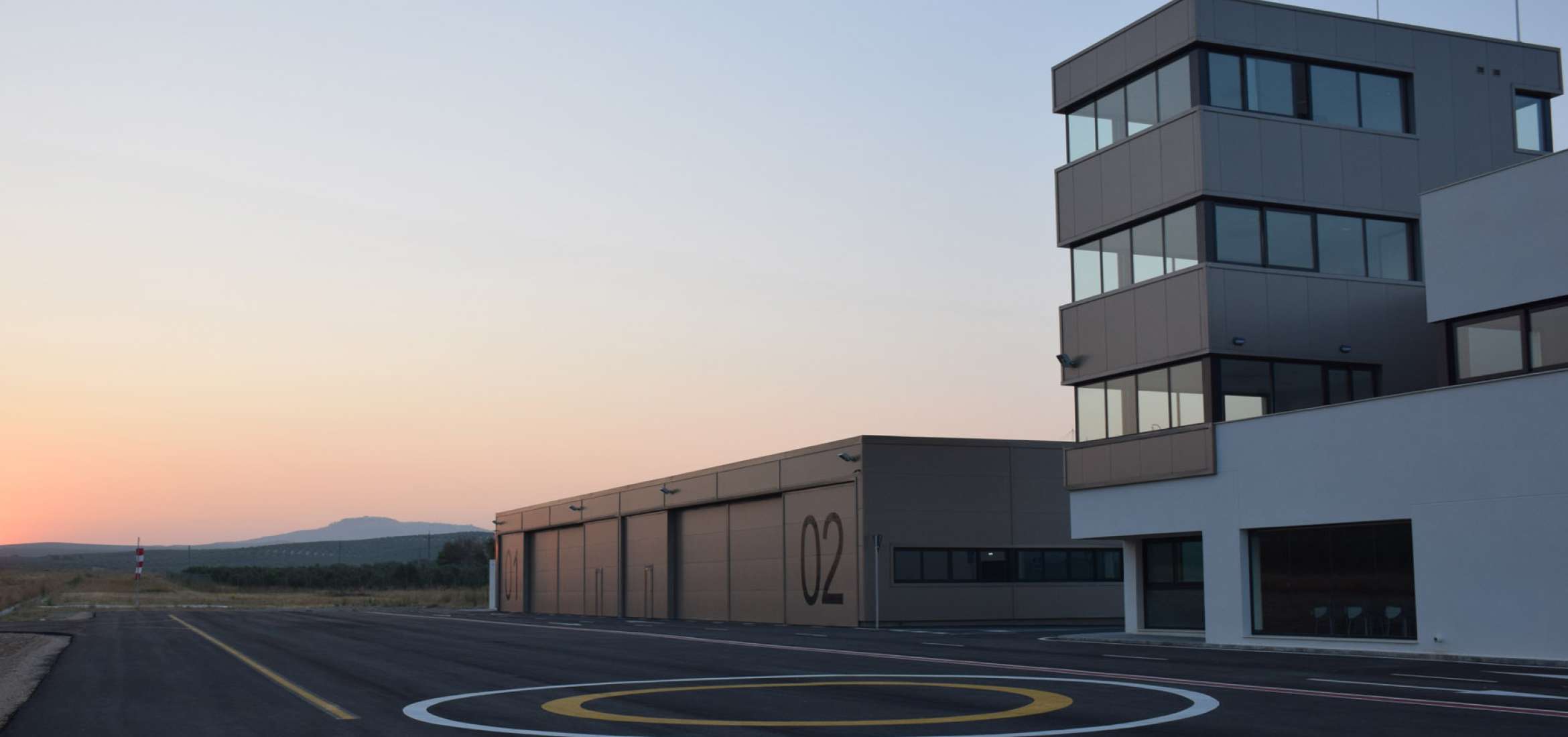

ATLAS
Universidad de Sevilla (USE)
Robotics, Vision and Control Group
ATLAS

Barcelona Robot Lab
Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC)
IRI
Barcelona Robot Lab
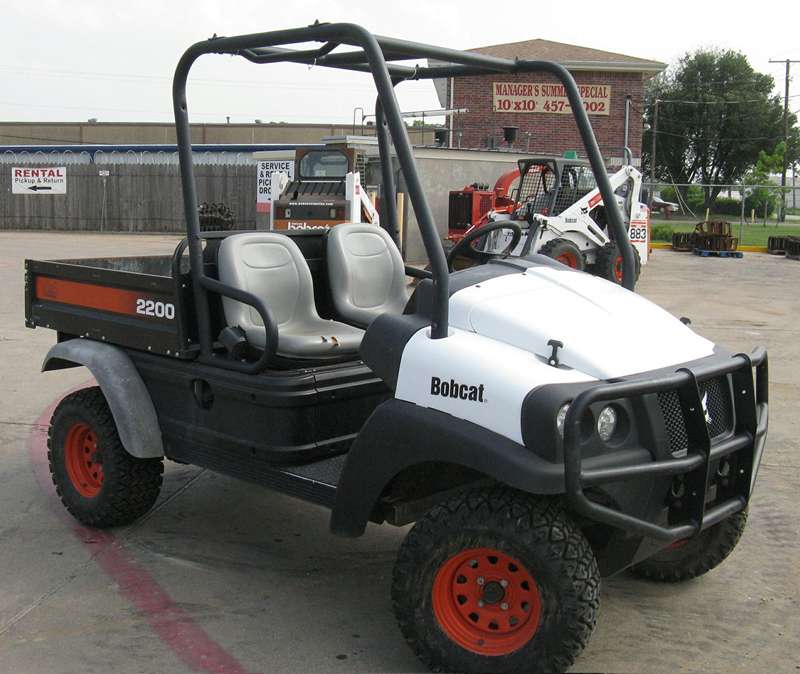

Bobcat
Universidad de Sevilla (USE)
Robotics, Vision and Control Group
Bobcat
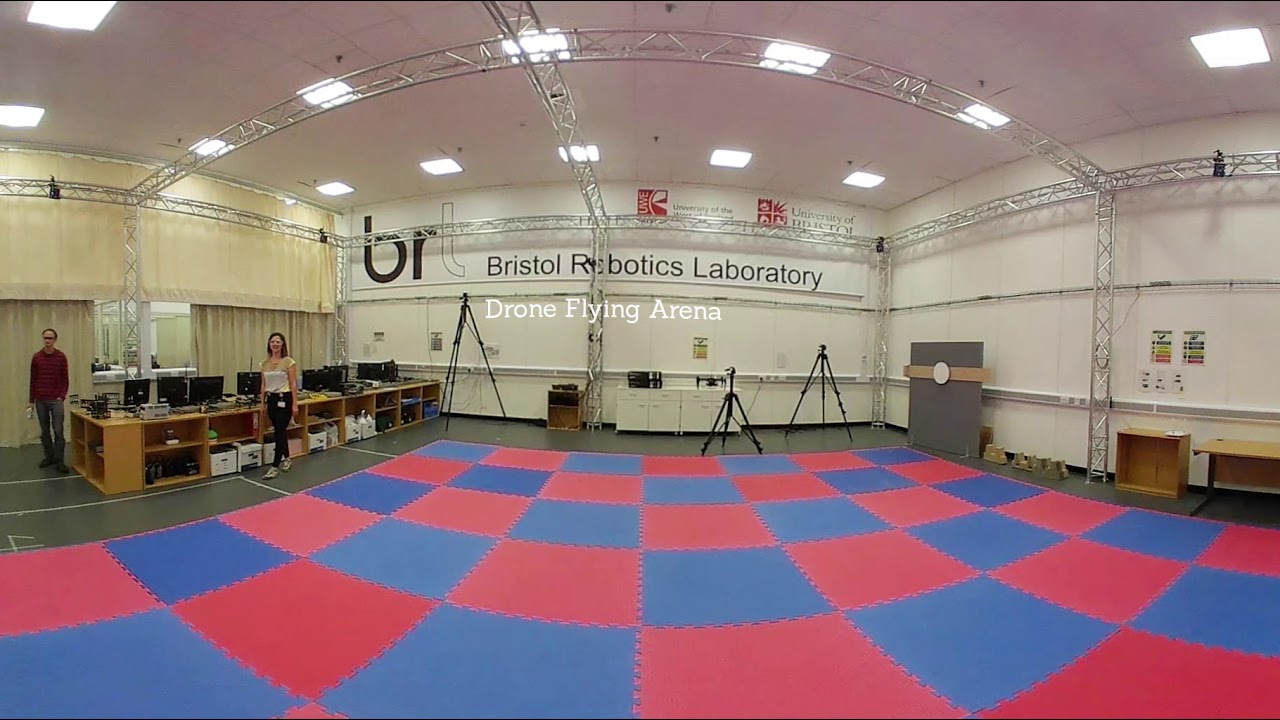

BRL – Flying Arena
University of the West of England (UWE Bristol)
Bristol Robotics Laboratory
BRL – Flying Arena
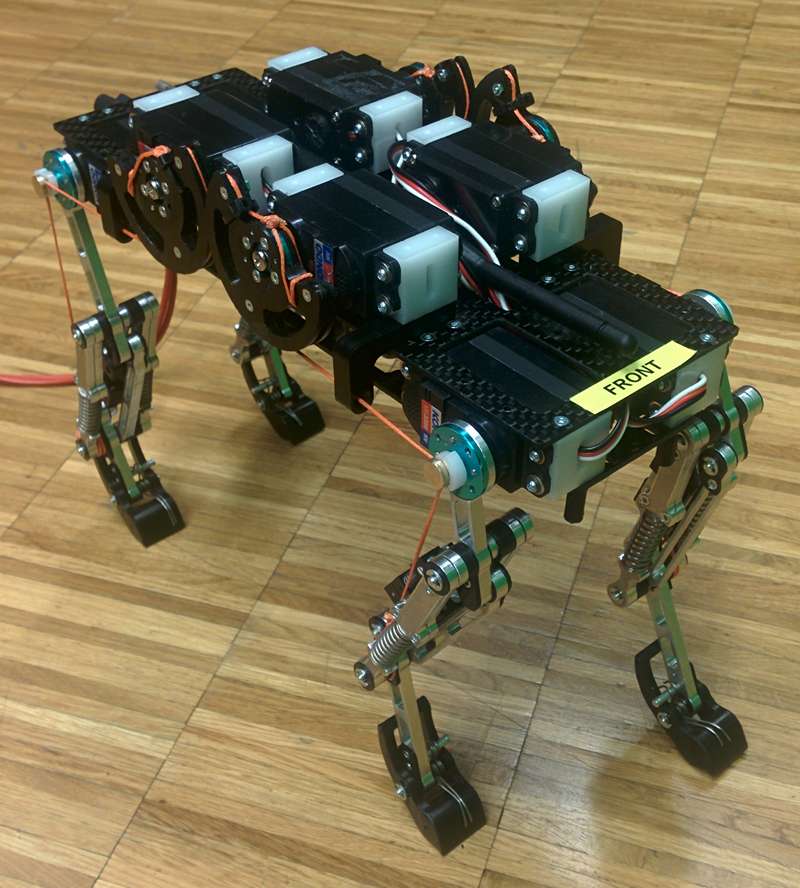

Cheetah-Cub-AL
École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL)
BioRobotics Lab
Cheetah-Cub-AL
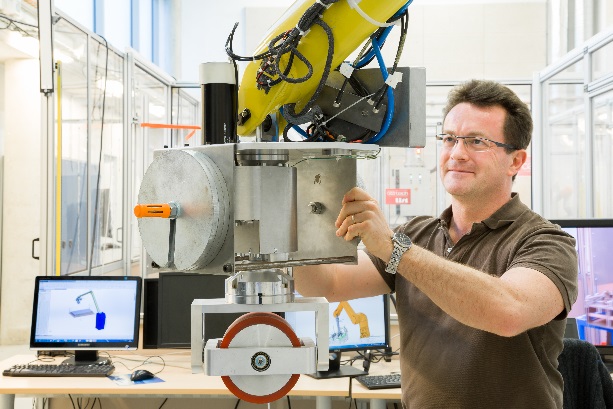

Cobomanip
Commissariat à l’Energie Atomique (CEA)
Interactive Robotics Lab
Cobomanip
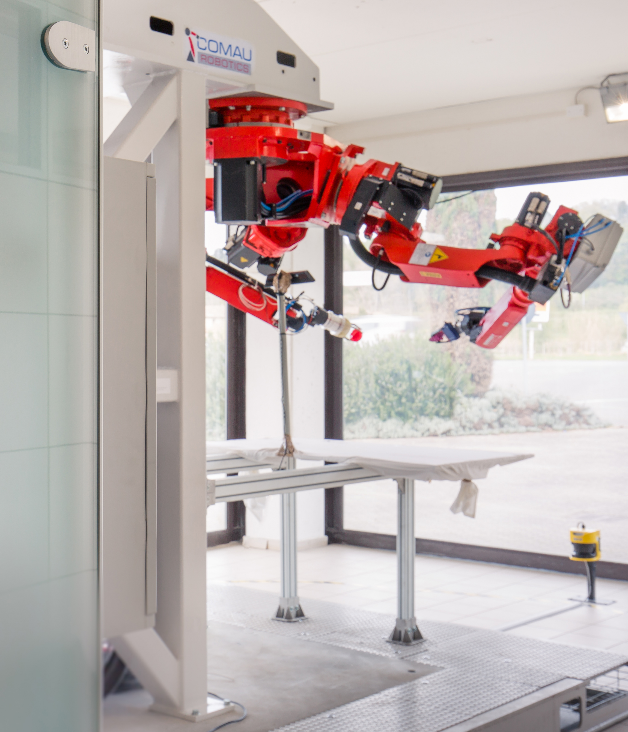

COMAU Dual arm robot
School of Advanced Studies Sant’Anna (SSSA)
The BioRobotics Institute
COMAU Dual arm robot
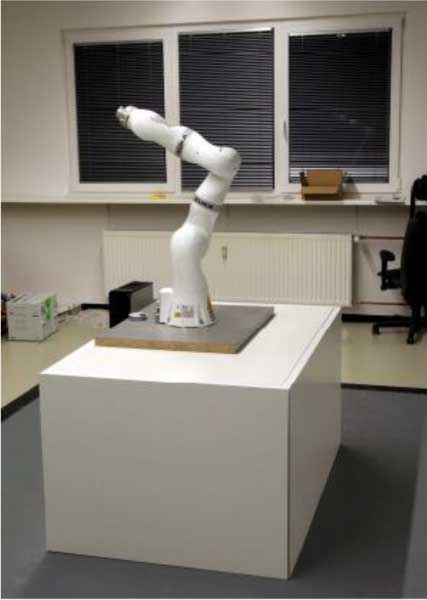

Cooperative Robotic Manufacturing Station
Technical University Munich (TUM)
Robotics and Embedded Systems
Cooperative Robotic Manufacturing Station
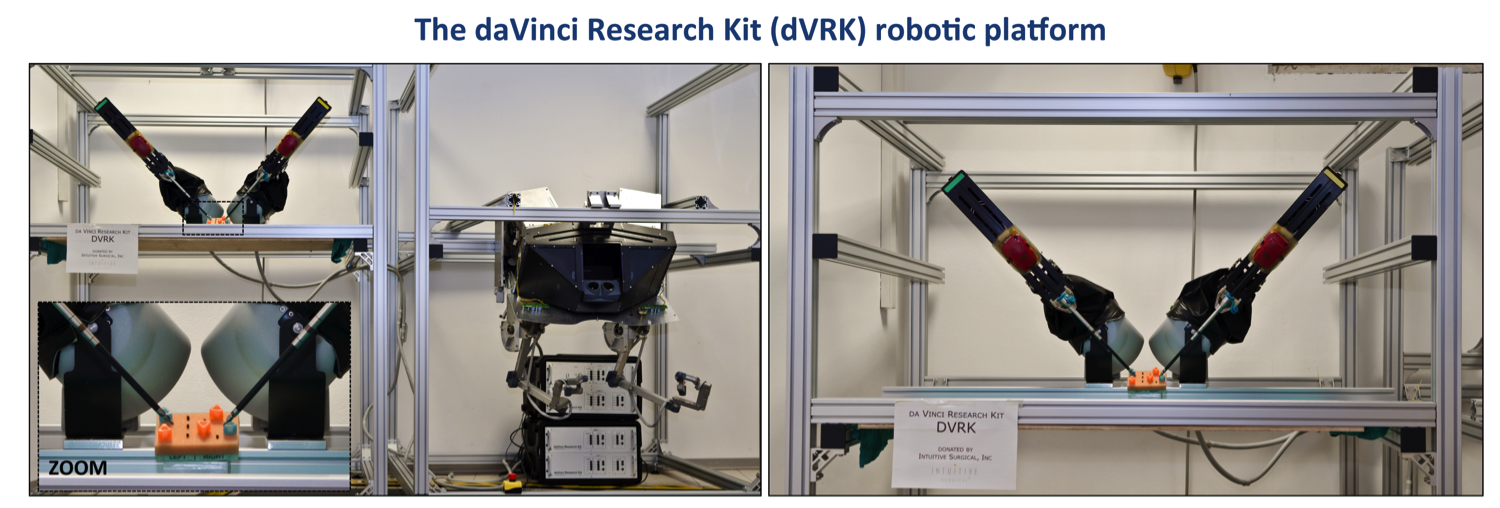
Da Vinci Research Kit (DVRK)
School of Advanced Studies Sant’Anna (SSSA)
The BioRobotics Institute
Da Vinci Research Kit (DVRK)
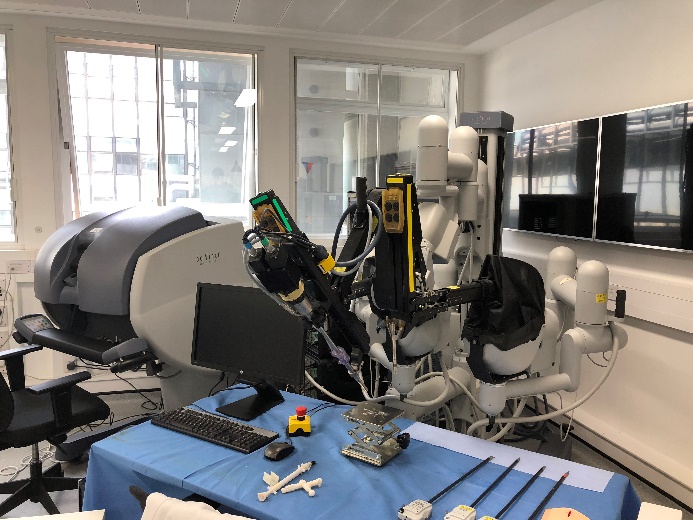

Da Vinci Research Kit (DVRK)
Imperial College London (IMPERIAL)
The Hamlyn Centre
Da Vinci Research Kit (DVRK)

Darius
Universidad de Sevilla (USE)
Robotics, Vision and Control Group
Darius

DJI F550
Universidad de Sevilla (USE)
Robotics, Vision and Control Group
DJI F550
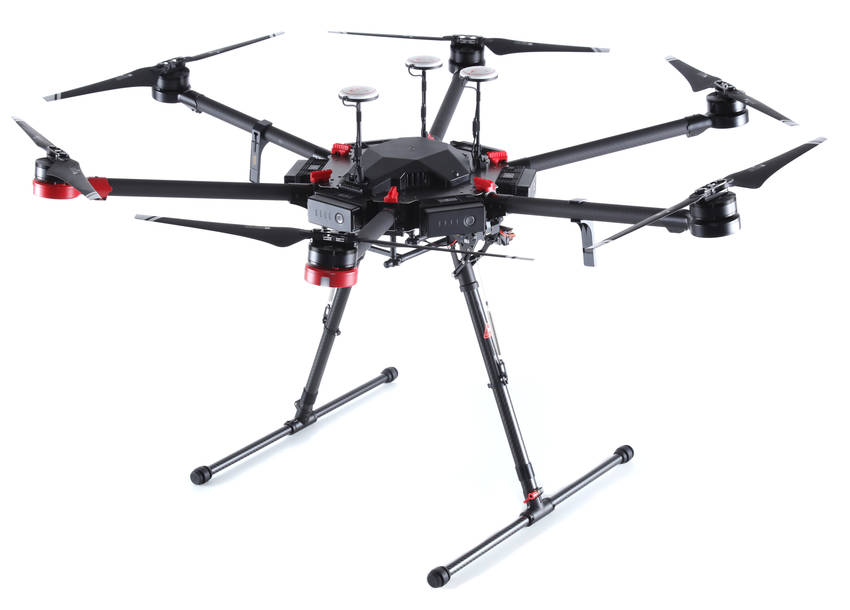

DJI Matrice 600
Universidad de Sevilla (USE)
Robotics, Vision and Control Group
DJI Matrice 600
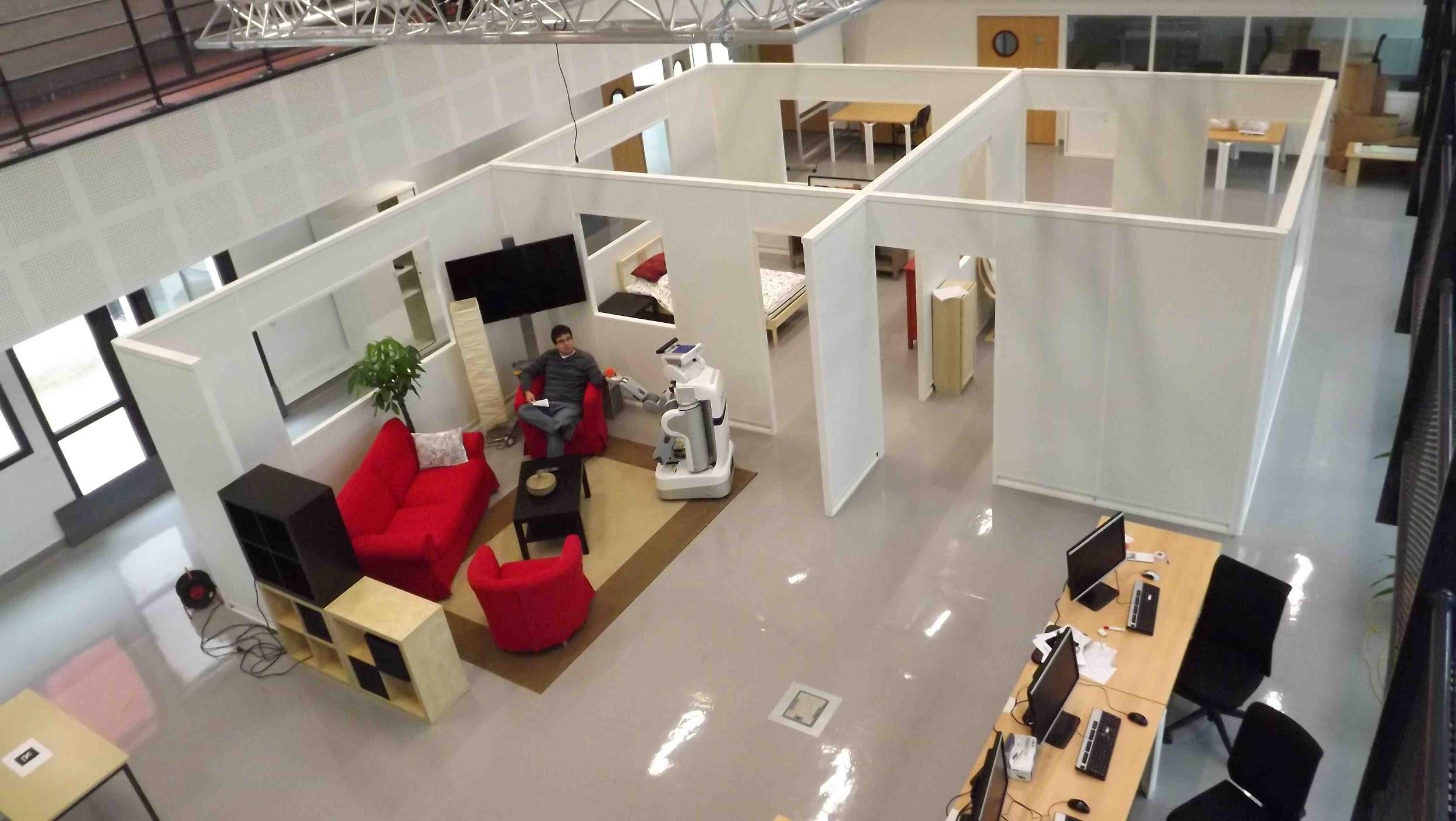

Domotic House
Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS)
The Department of Robotics of LAAS
Domotic House
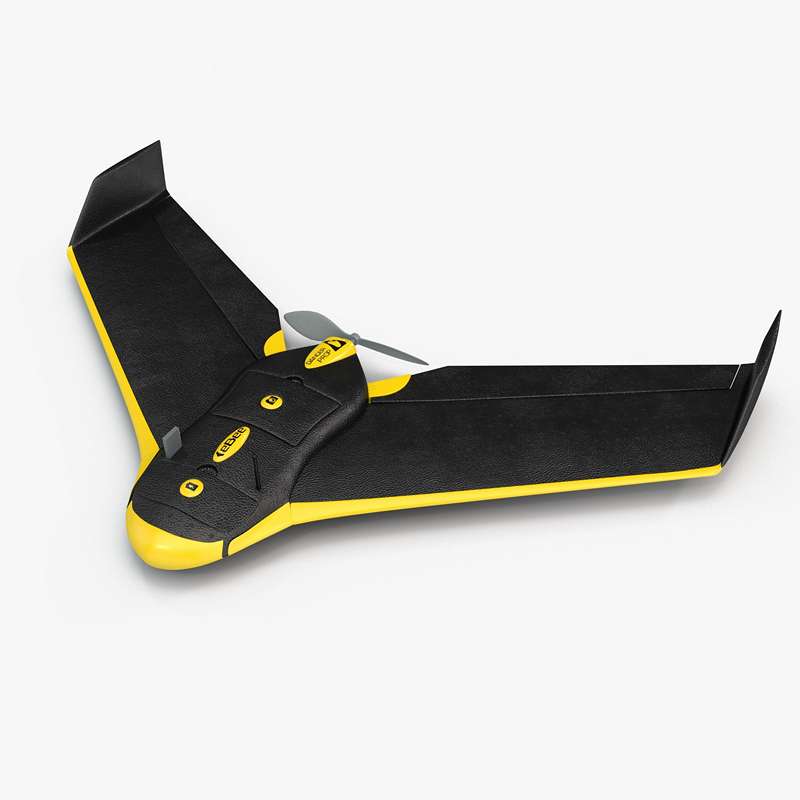

eBee drone
École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL)
Laboratory of Intelligent Systems
eBee drone
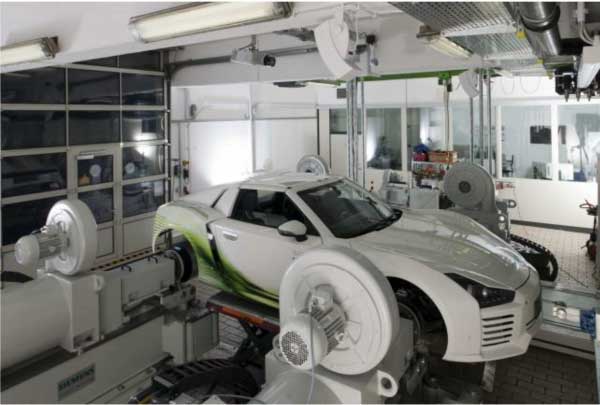

Electric Car Testbed
Technical University Munich (TUM)
Robotics and Embedded Systems
Electric Car Testbed
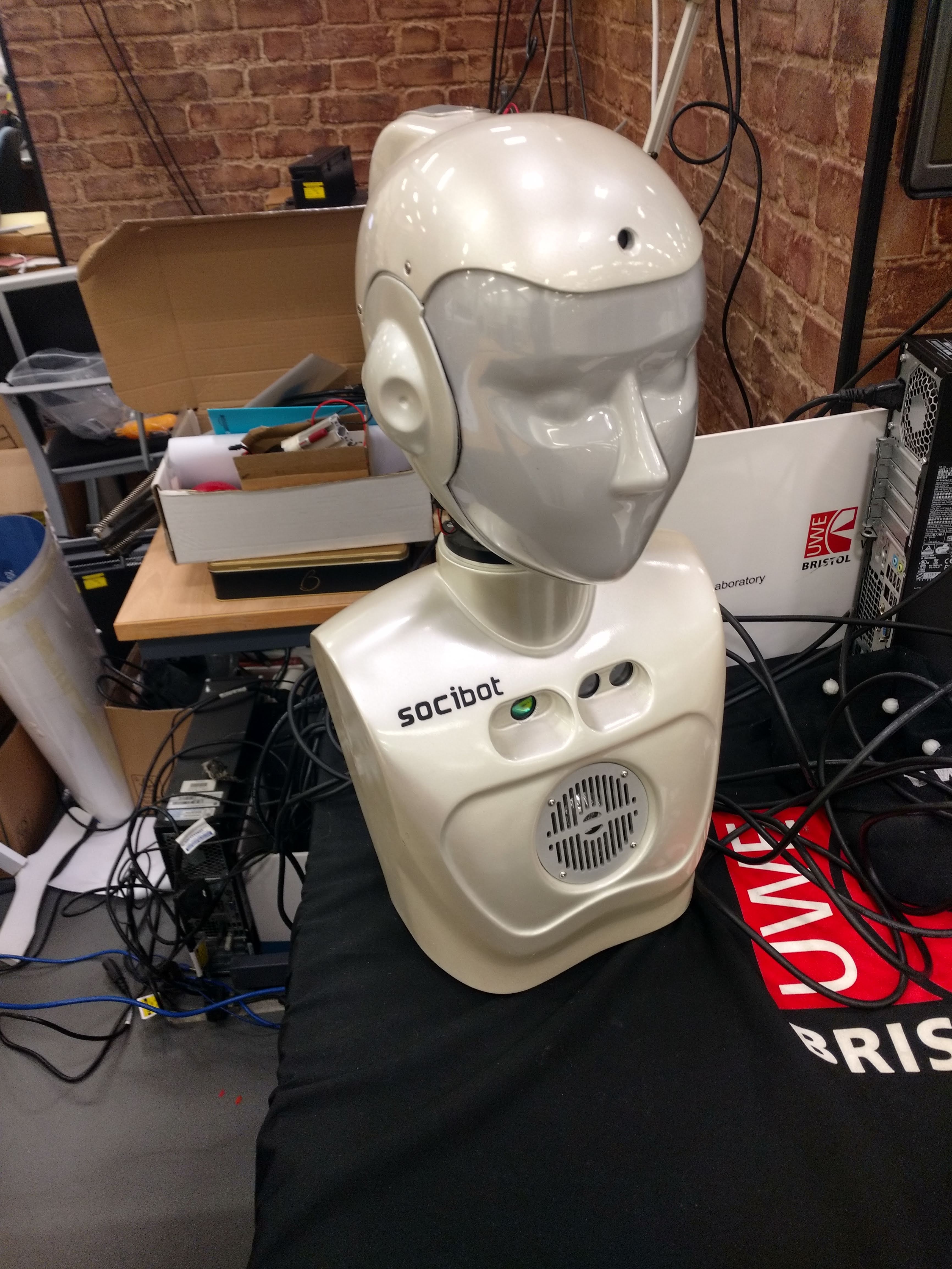

Engineered Arts – SociBot mini
University of the West of England (UWE Bristol)
Ambient Assisted Living Laboratory
Engineered Arts – SociBot mini
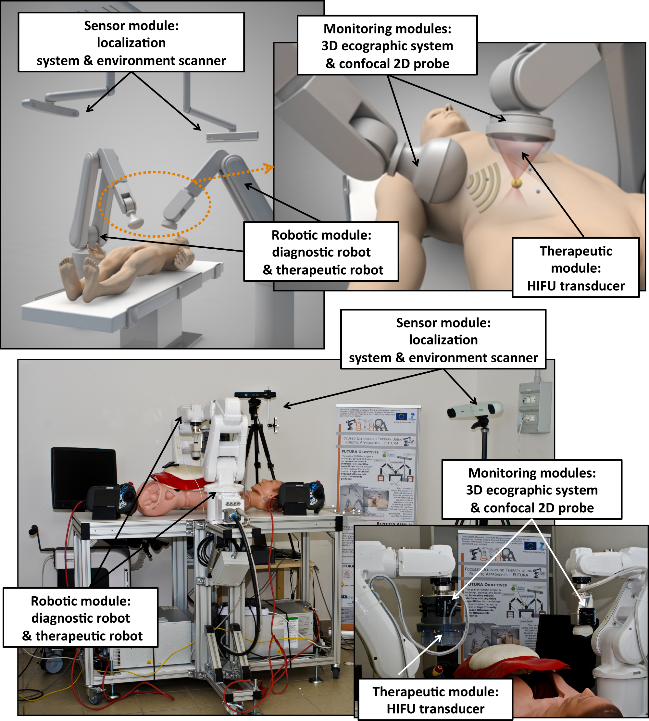
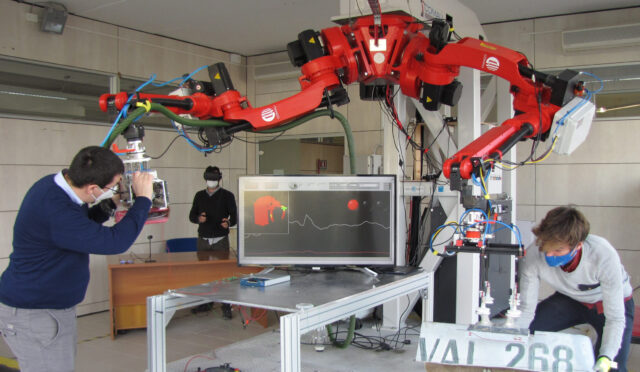
FUTURA platform for US-guided HIFU treatment
School of Advanced Studies Sant’Anna (SSSA)
The BioRobotics Institute
FUTURA platform for US-guided HIFU treatment

Haption ABLE
Commissariat à l’Energie Atomique (CEA)
Interactive Robotics Lab
Haption ABLE
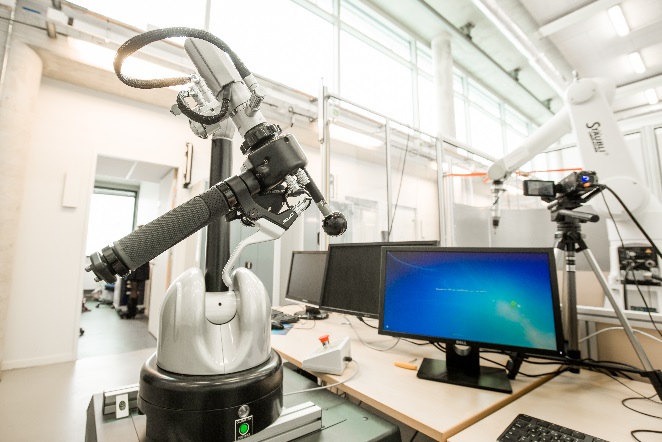

Haption Virtuose 6D
Commissariat à l’Energie Atomique (CEA)
Interactive Robotics Lab
Haption Virtuose 6D

HMI Human media interaction lab facilities
University of Twente (UT)
Department of Robotics
HMI Human media interaction lab facilities

Human Motion Analysis with Vicon
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT)
Institute of Anthropomatics and Robotics – High Performance Humanoid Technologies Lab (IAR H2T)
Human Motion Analysis with Vicon
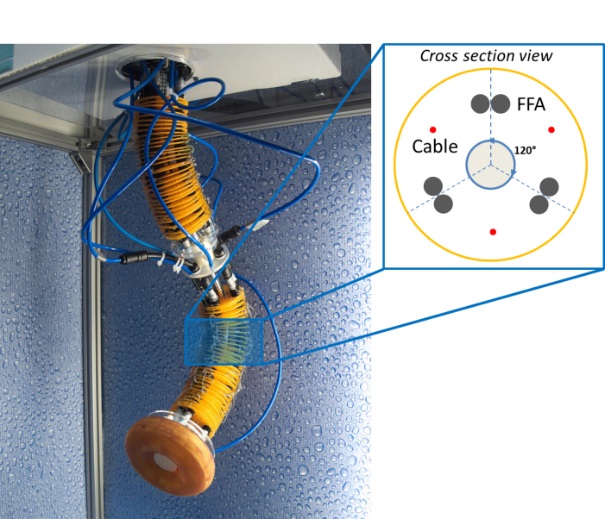
I-Support soft arm
School of Advanced Studies Sant’Anna (SSSA)
The BioRobotics Institute
I-Support soft arm
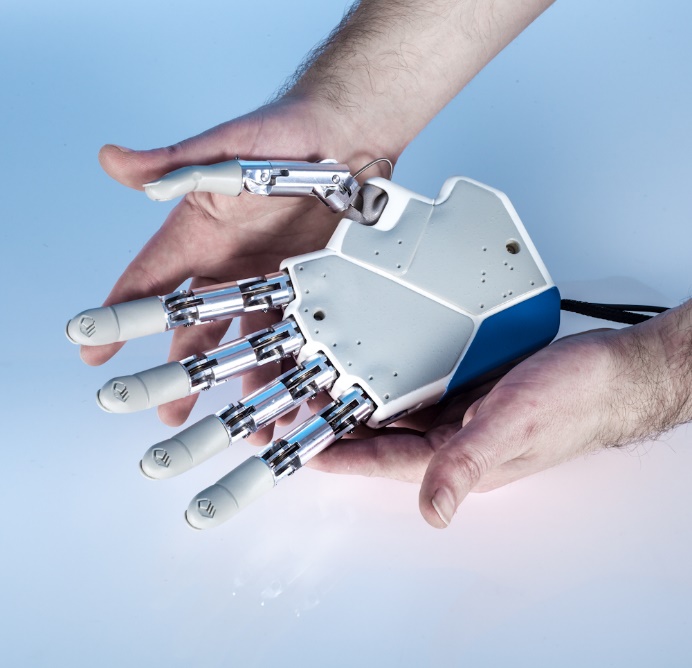

IH2 Azzurra Hand
School of Advanced Studies Sant’Anna (SSSA)
The BioRobotics Institute
IH2 Azzurra Hand

Indoor robots
Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS)
The Department of Robotics of LAAS
Indoor robots

InMotion wrist
School of Advanced Studies Sant’Anna (SSSA)
The BioRobotics Institute
InMotion wrist
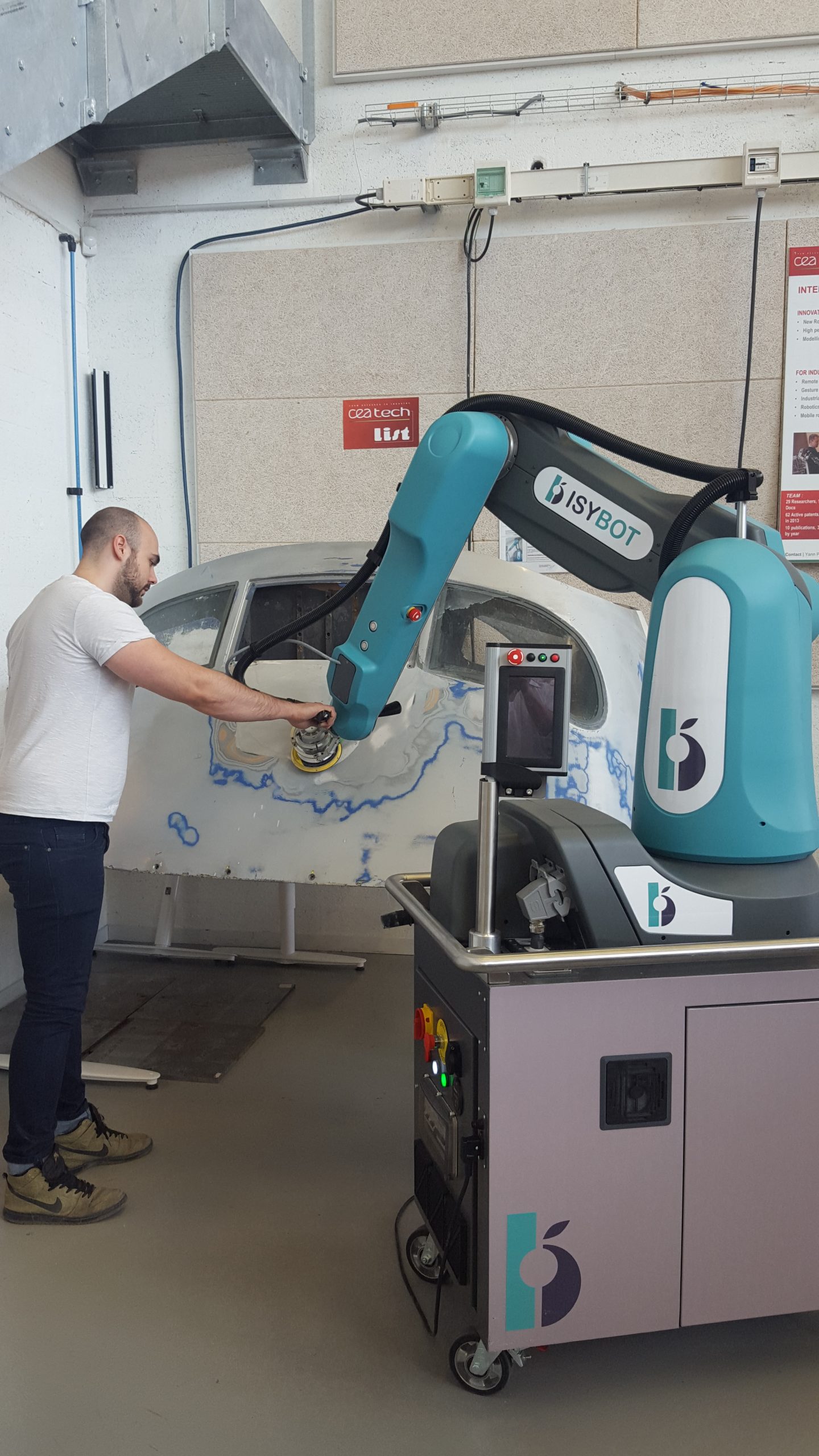

Isybot Syb 3
Commissariat à l’Energie Atomique (CEA)
Interactive Robotics Lab
Isybot Syb 3
Through agile automation, SYBOT simplifies the response to flexibility and variability requirements for all types of processes such as grinding.
SYBOT interactive COBOTs improve productivity while reducing operator fatigue.

IVO
Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC)
IRI
IVO

Kawada Robotics HRP-2
Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS)
The Department of Robotics of LAAS
Kawada Robotics HRP-2
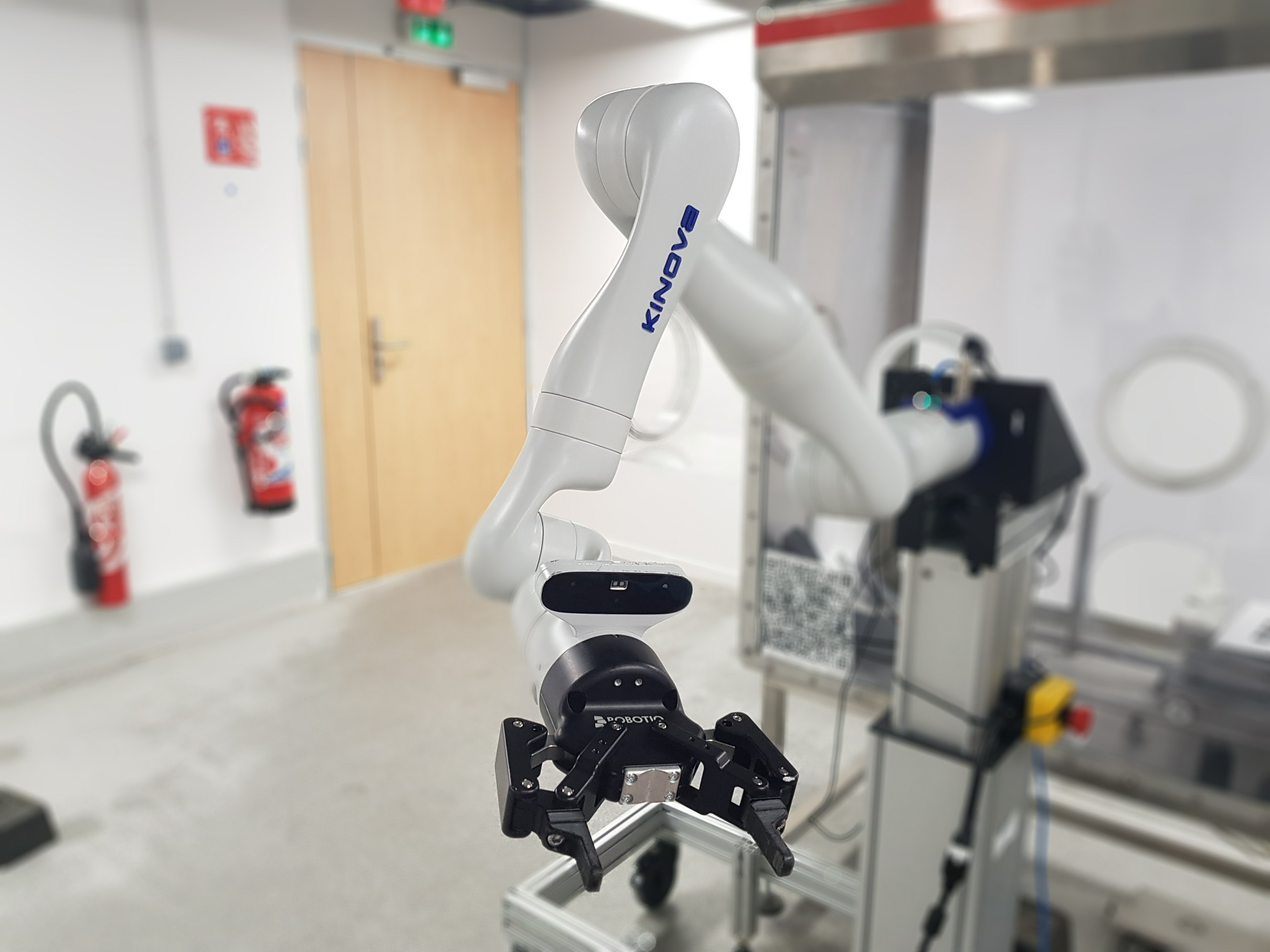

Kinova Gen3
Commissariat à l’Energie Atomique (CEA)
Interactive Robotics Lab
Kinova Gen3
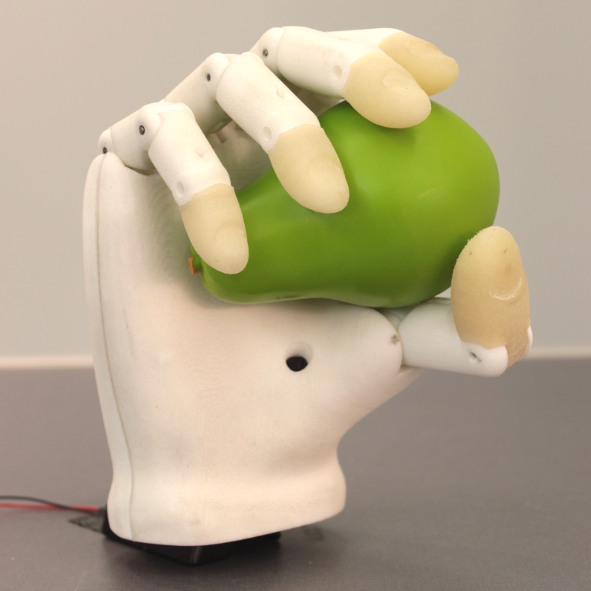
KIT Prosthetic Hand
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT)
Institute of Anthropomatics and Robotics – High Performance Humanoid Technologies Lab (IAR H2T)
KIT Prosthetic Hand
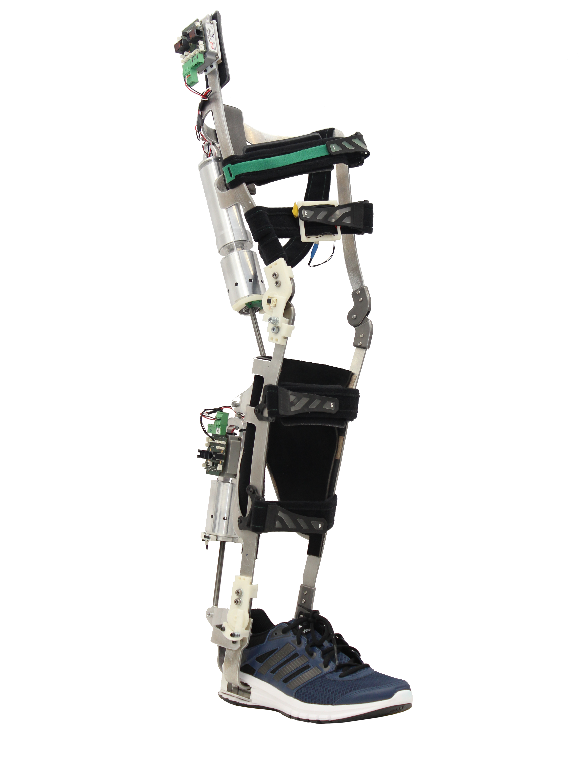

KIT-EXO-1
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT)
Institute of Anthropomatics and Robotics – High Performance Humanoid Technologies Lab (IAR H2T)
KIT-EXO-1
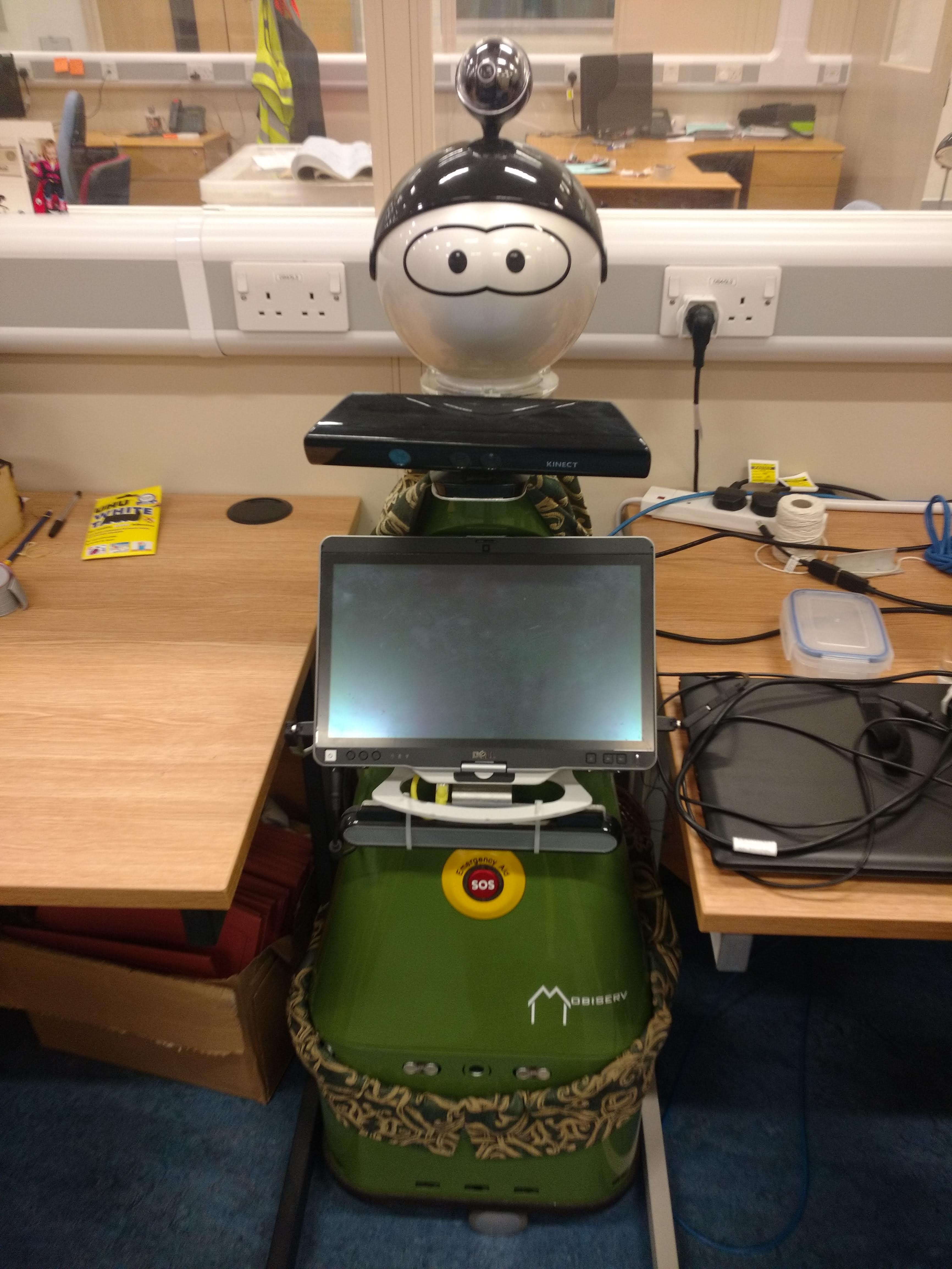

KOMPAÏ Robots – KOMPAÏ 1
University of the West of England (UWE Bristol)
Ambient Assisted Living Laboratory
KOMPAÏ Robots – KOMPAÏ 1
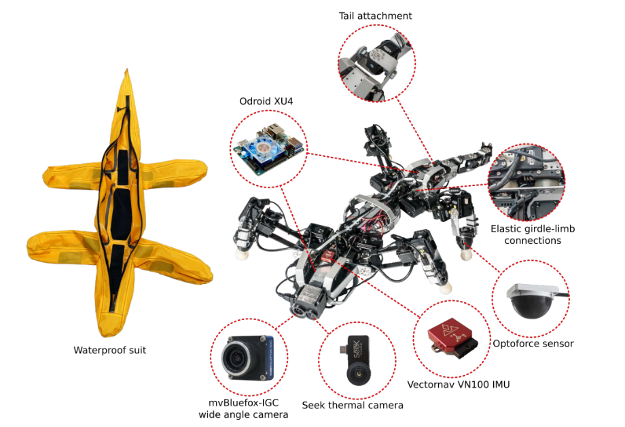
Krock-2 Amphibious Quadruped
École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL)
BioRobotics Lab
Krock-2 Amphibious Quadruped
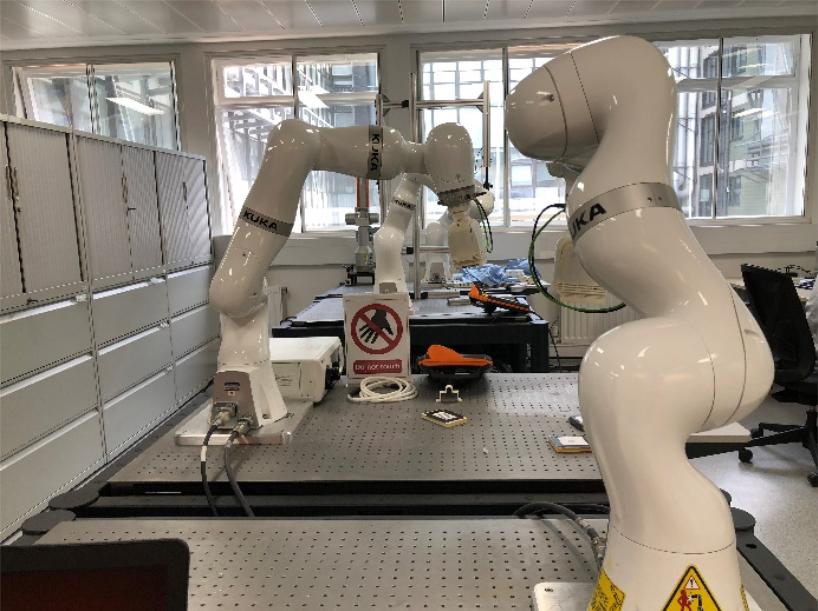

KUKA iiwa7 r800/iiwa14 r820 Platform
Imperial College London (IMPERIAL)
The Hamlyn Centre
KUKA iiwa7 r800/iiwa14 r820 Platform
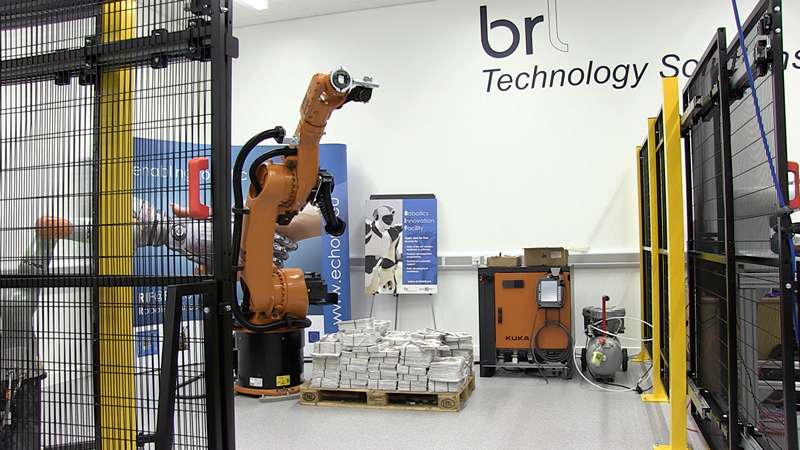

KUKA KR60-3
University of the West of England (UWE Bristol)
Robotics Innovation Facility
KUKA KR60-3

Laboratory space (equipment)
Instituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT)
iCub Facility
Laboratory space (equipment)

LeQuad quadcopter
École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL)
Laboratory of Intelligent Systems
LeQuad quadcopter
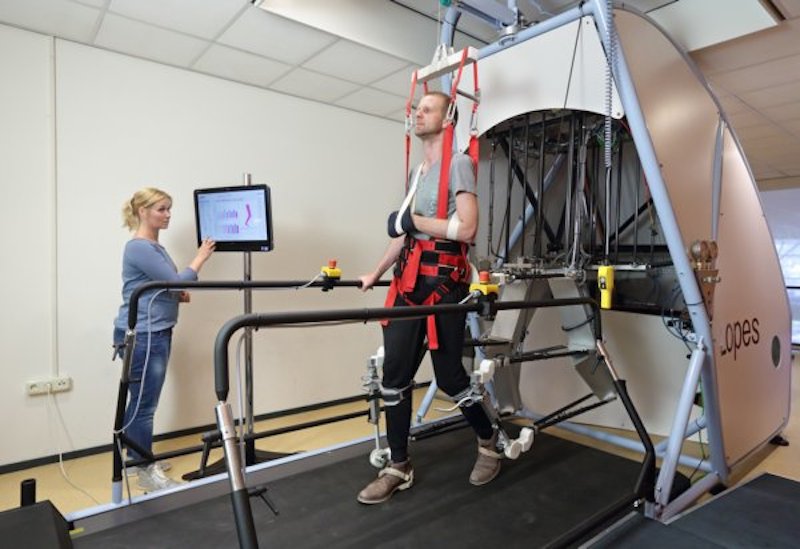

LOPES
University of Twente (UT)
Department of Robotics
LOPES
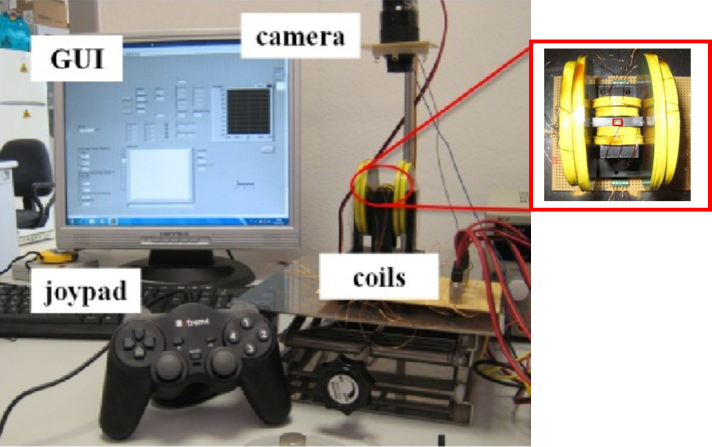
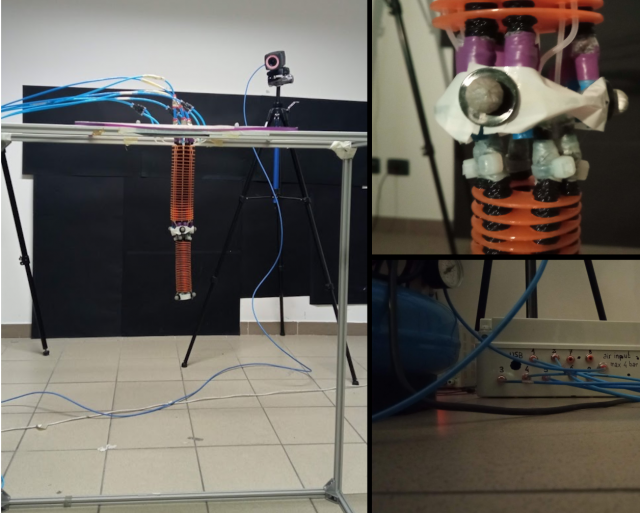
Magnetic Micro Manipulation Platform
School of Advanced Studies Sant’Anna (SSSA)
The BioRobotics Institute
Magnetic Micro Manipulation Platform
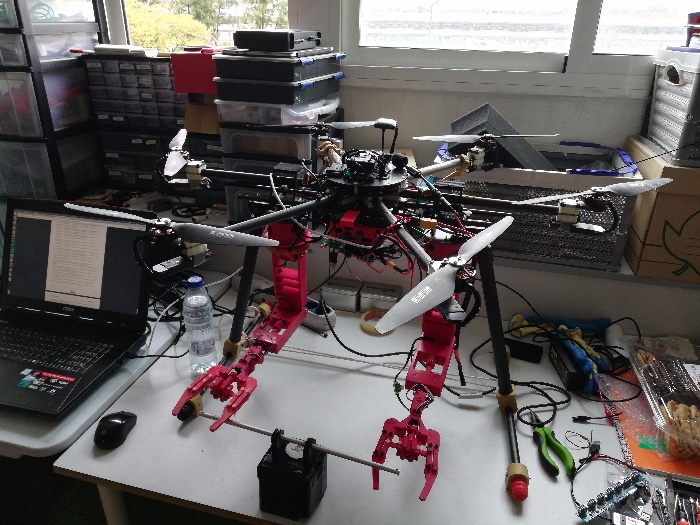

MBZIRC Hexarotor
Universidad de Sevilla (USE)
Robotics, Vision and Control Group
MBZIRC Hexarotor
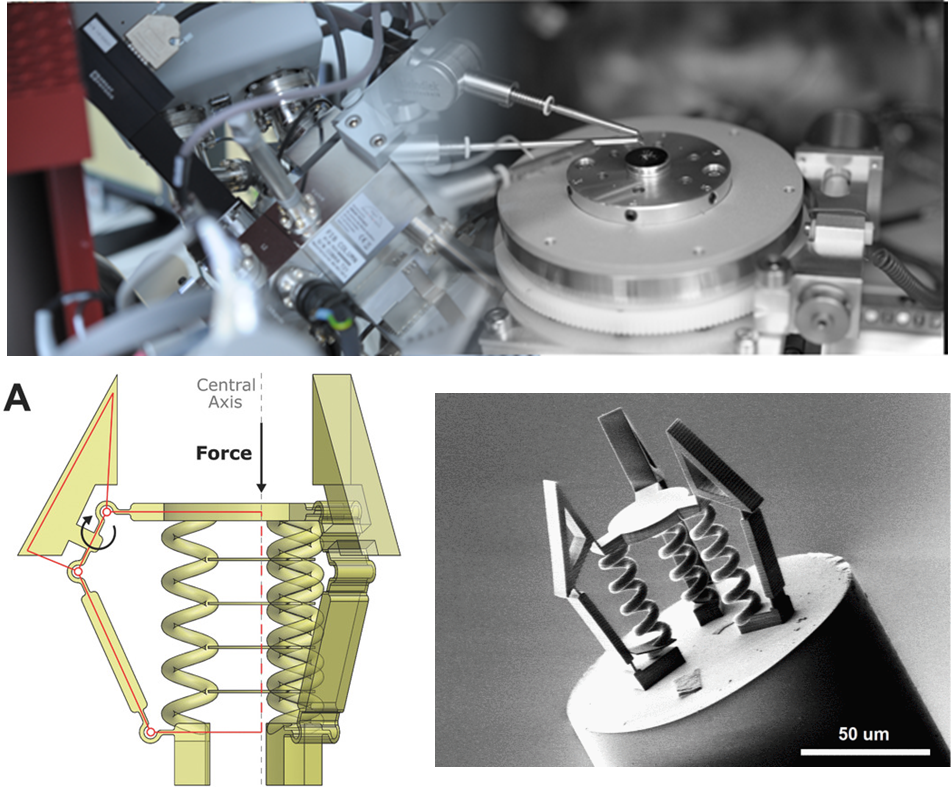
Micro-Robot Fabrication and Characterisation
Imperial College London (IMPERIAL)
The Hamlyn Centre
Micro-Robot Fabrication and Characterisation
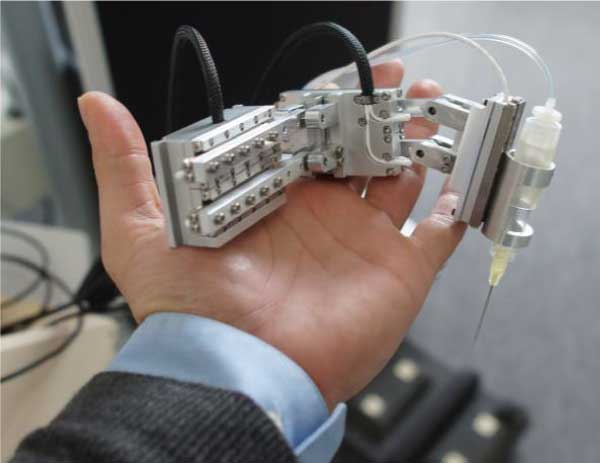
Microsurgical Robot
Technical University Munich (TUM)
Robotics and Embedded Systems
Microsurgical Robot

Motion capture and virtual reality platform
Imperial College London (IMPERIAL)
The Hamlyn Centre
Motion capture and virtual reality platform

Motion capture arena
École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL)
Laboratory of Intelligent Systems
Motion capture arena

Motion Capture Facilities
Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS)
The Department of Robotics of LAAS
Motion Capture Facilities
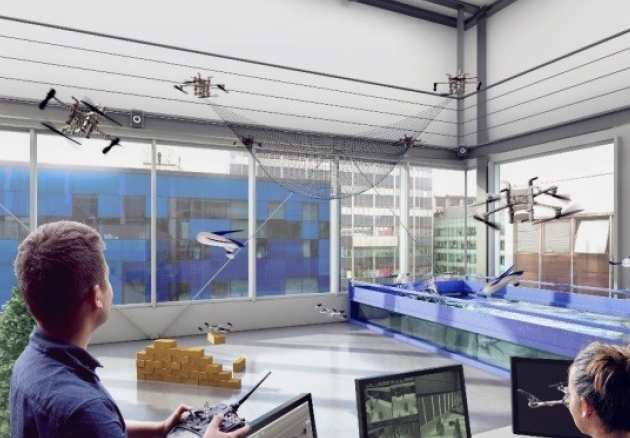

Multi Terrain Flight Arena
Imperial College London (IMPERIAL)
The Hamlyn Centre
Multi Terrain Flight Arena

NAO Robots
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT)
Institute of Anthropomatics and Robotics – High Performance Humanoid Technologies Lab (IAR H2T)
NAO Robots
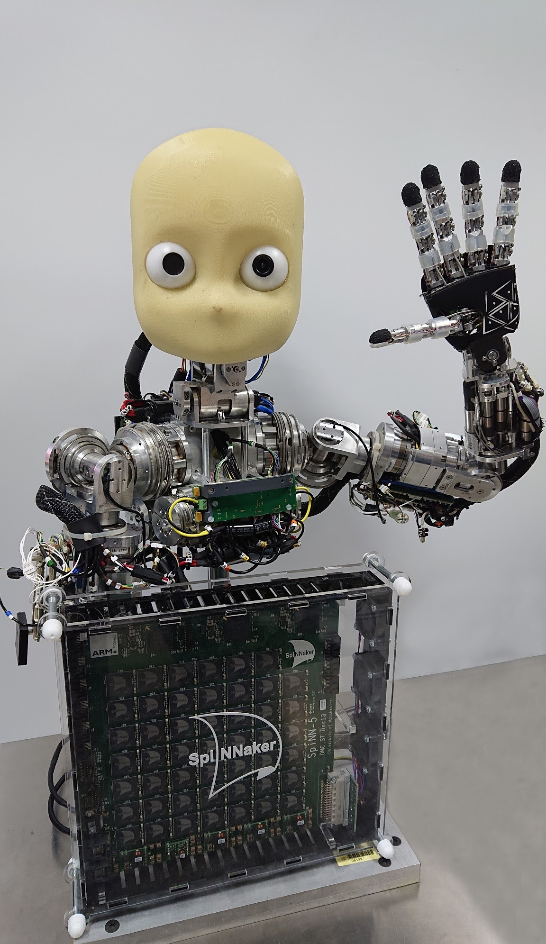
NeuiCub
School of Advanced Studies Sant’Anna (SSSA)
The BioRobotics Institute
NeuiCub
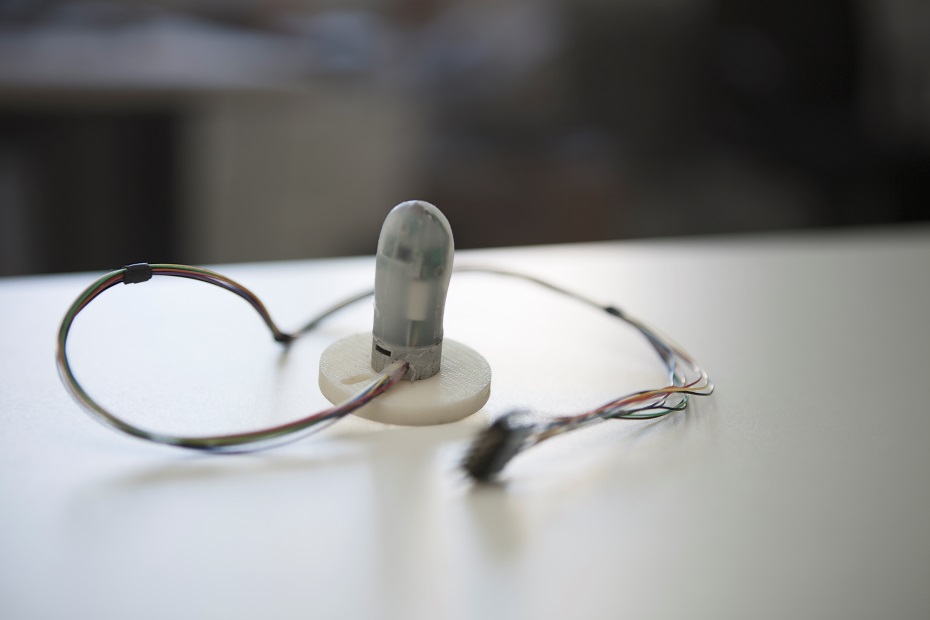

Neuromorphic Artificial Touch Sensors
School of Advanced Studies Sant’Anna (SSSA)
The BioRobotics Institute
Neuromorphic Artificial Touch Sensors
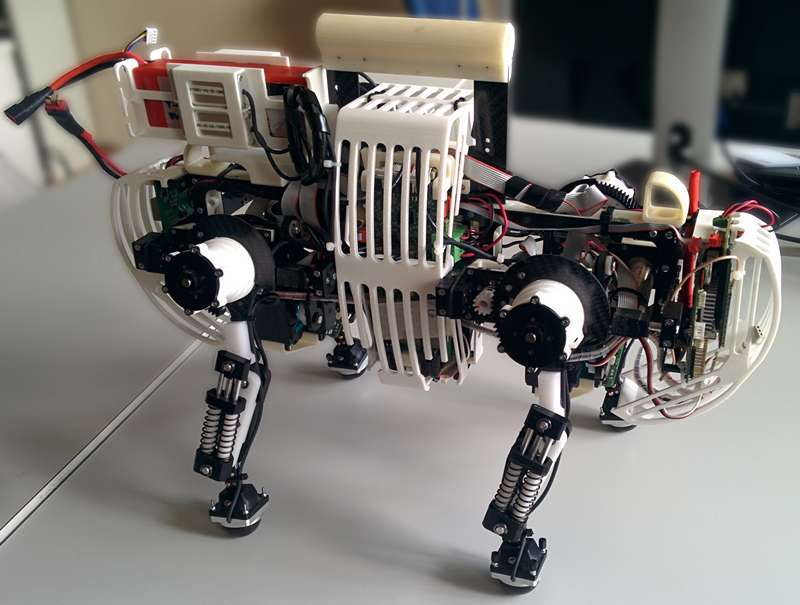
Oncilla
École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL)
BioRobotics Lab
Oncilla
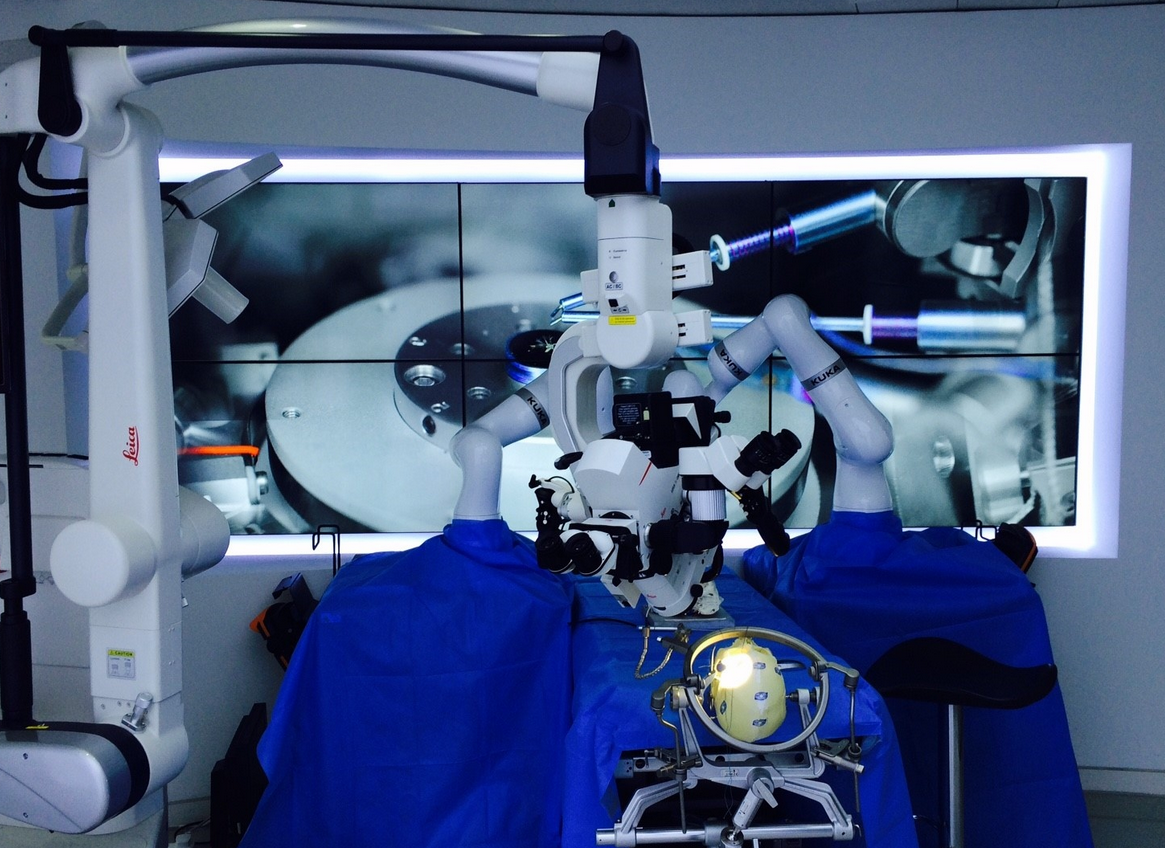
Operation room environment for medical robot prototype
Imperial College London (IMPERIAL)
The Hamlyn Centre
Operation room environment for medical robot prototype

Optitrack indoor testbed
Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC)
IRI
Optitrack indoor testbed
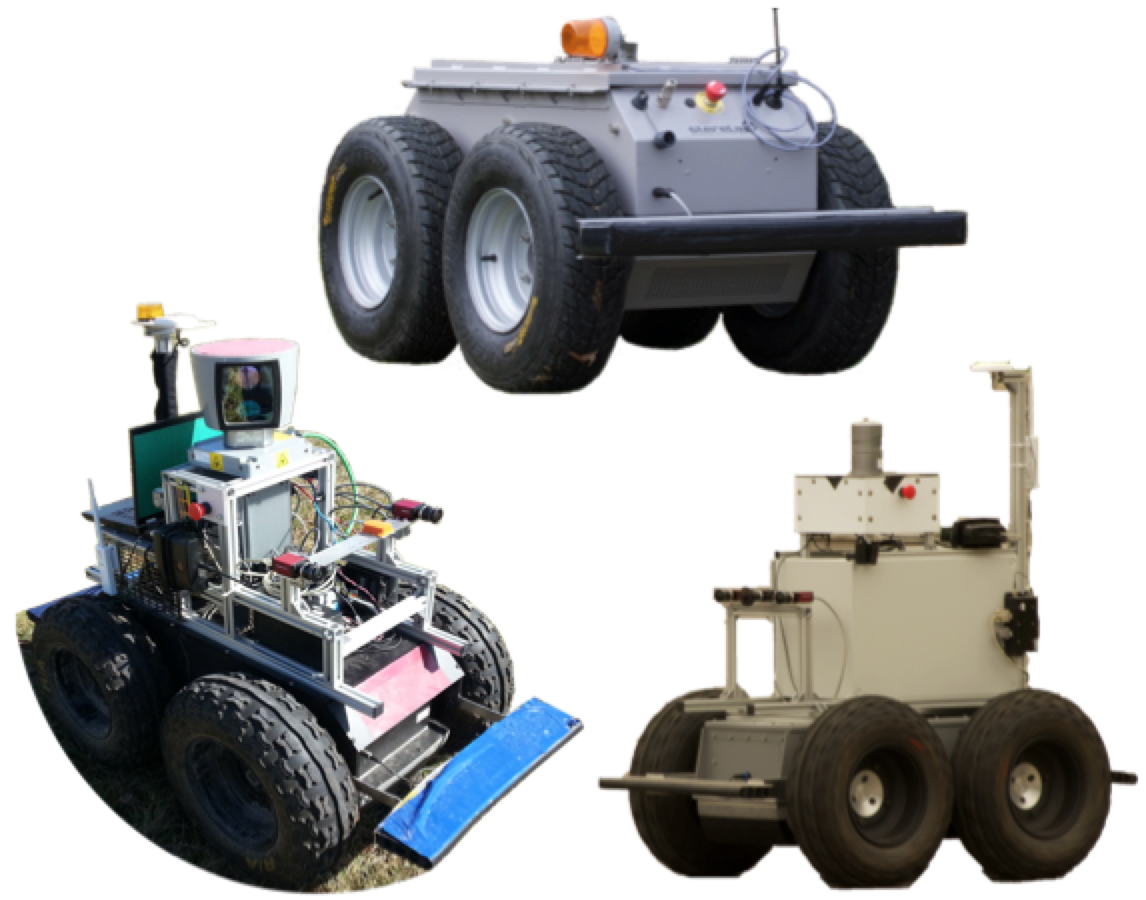

Outdoor robots
Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS)
The Department of Robotics of LAAS
Outdoor robots

PAL Robotics Pyrène
Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS)
The Department of Robotics of LAAS
PAL Robotics Pyrène
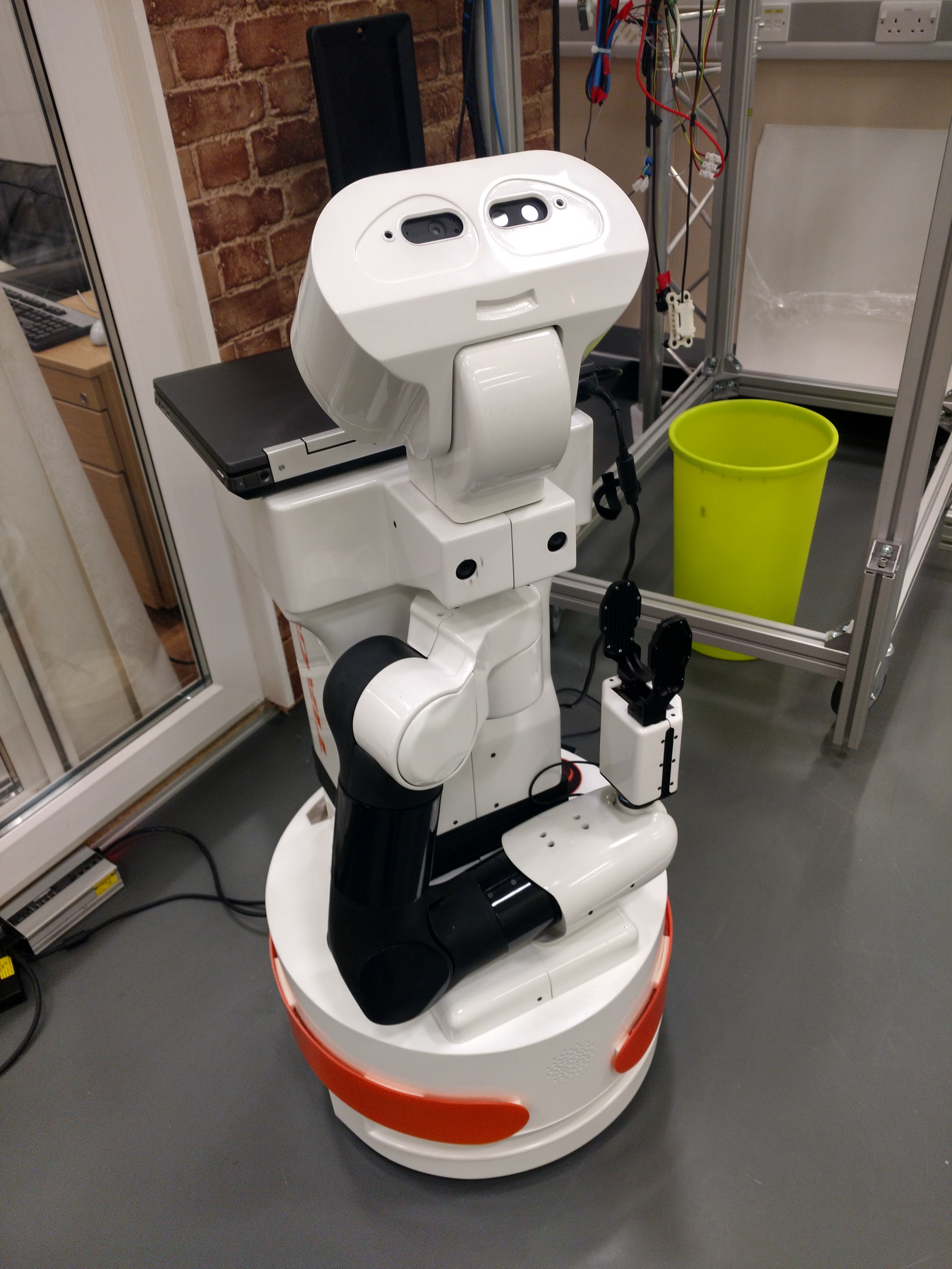

PAL Robotics Tiago
University of the West of England (UWE Bristol)
Bristol Robotics Laboratory
PAL Robotics Tiago

Pioneer 3-AT
Universidad de Sevilla (USE)
Robotics, Vision and Control Group
Pioneer 3-AT
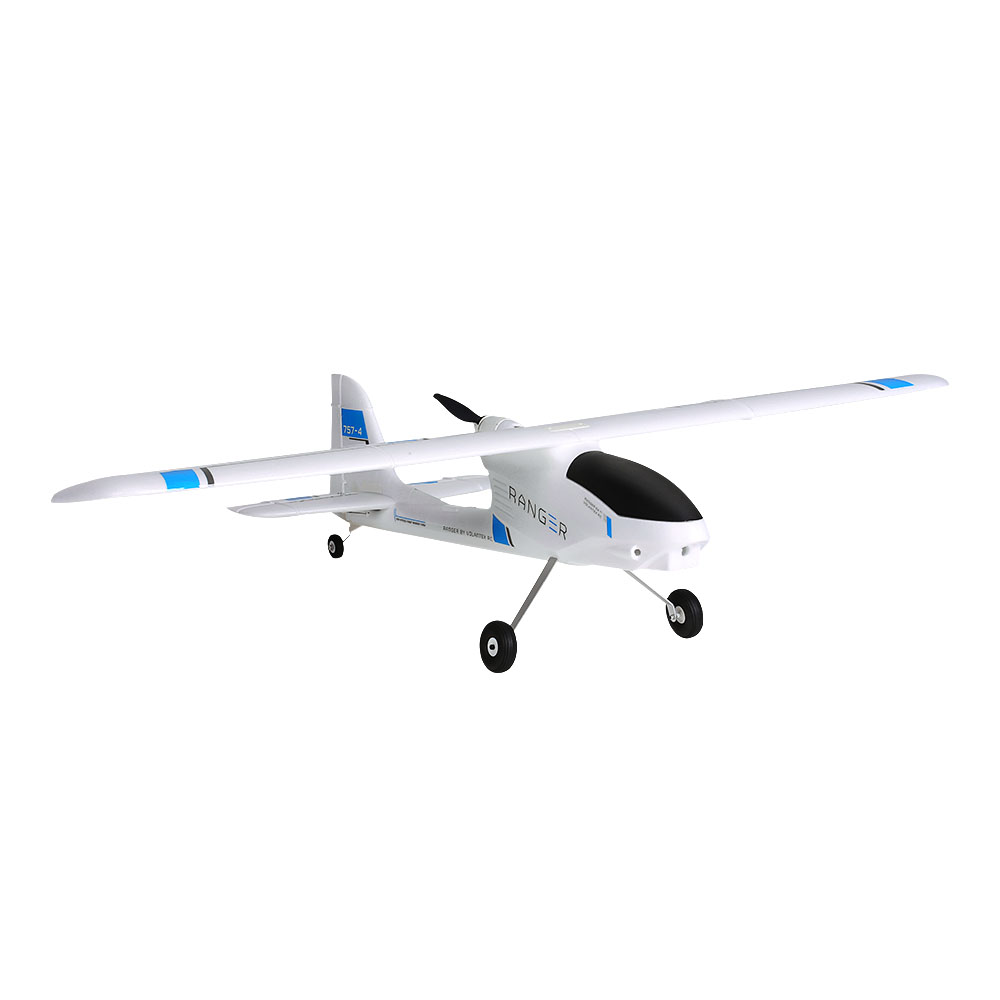

Ranger
Universidad de Sevilla (USE)
Robotics, Vision and Control Group
Ranger
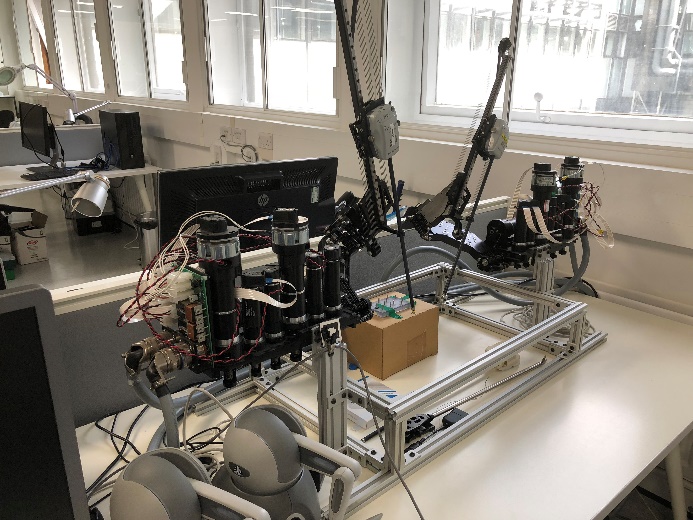

RAVEN II Surgical Robot
Imperial College London (IMPERIAL)
The Hamlyn Centre
RAVEN II Surgical Robot
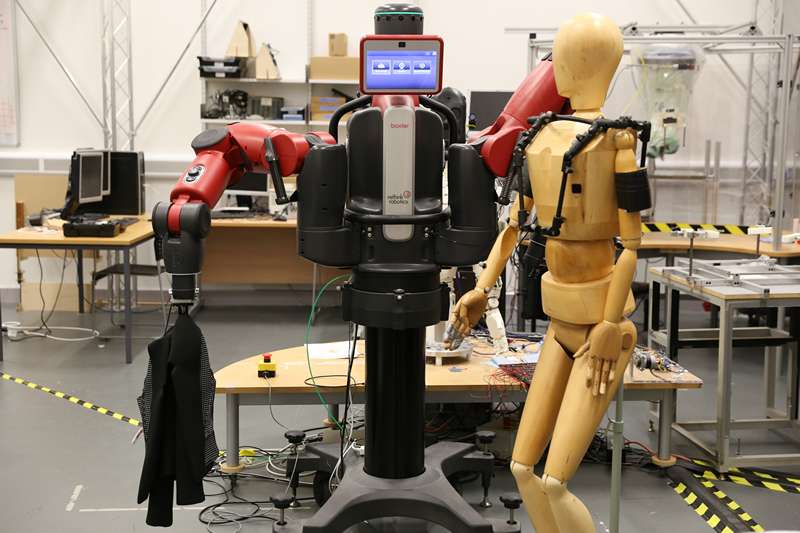

Rethink Robotics Baxter
University of the West of England (UWE Bristol)
Robotics Innovation Facility
Rethink Robotics Baxter

RoboGen
École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL)
Laboratory of Intelligent Systems
RoboGen
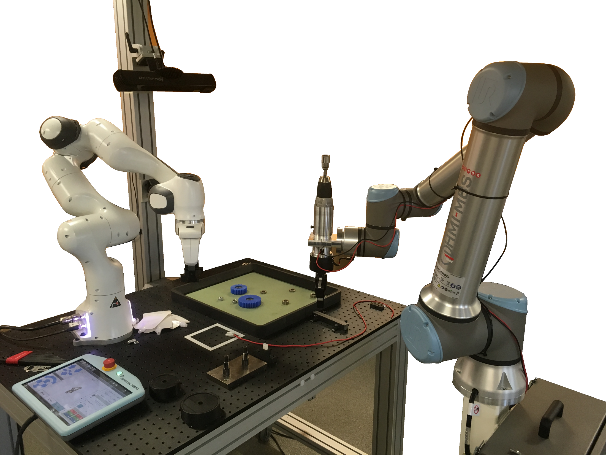
Robot Companion
Commissariat à l’Energie Atomique (CEA)
Interactive Robotics Lab
Robot Companion
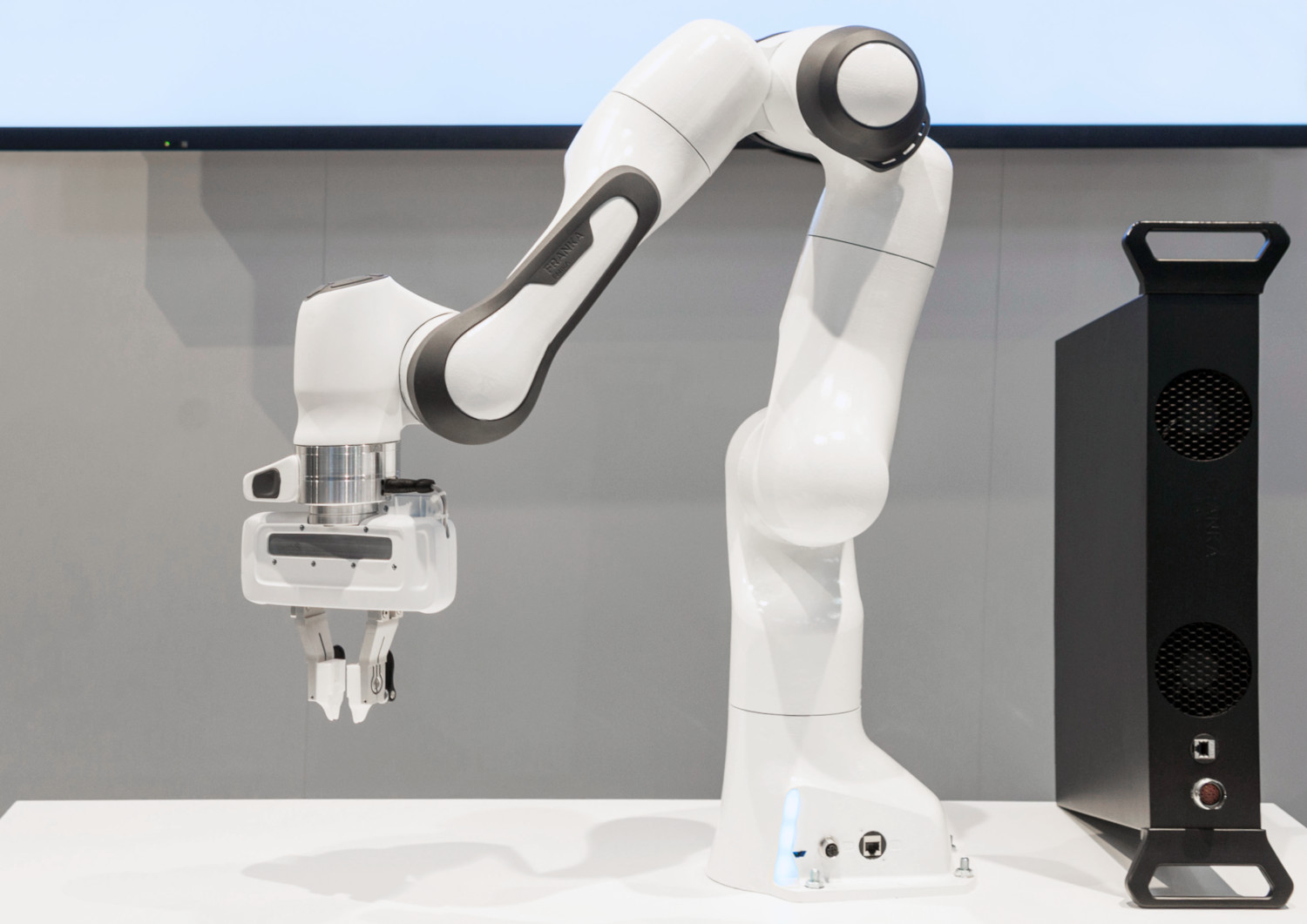

Robotic arms: Franka Emica
University of Twente (UT)
Department of Robotics
Robotic arms: Franka Emica
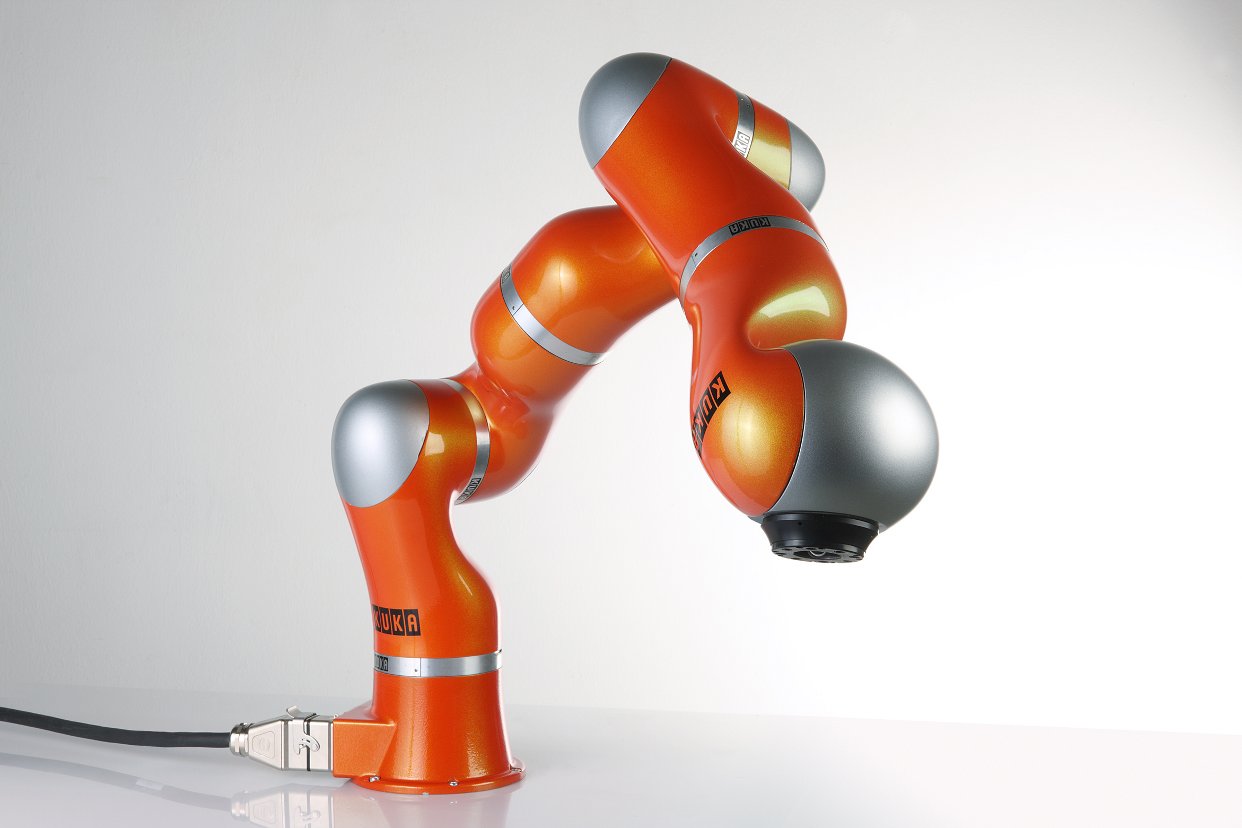

Robotic arms: KUKA LBR4+
University of Twente (UT)
Department of Robotics
Robotic arms: KUKA LBR4+
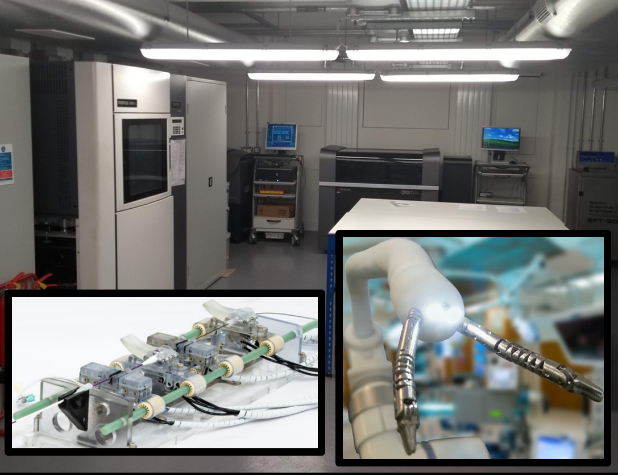

Robotic Fast Prototyping Platform
Imperial College London (IMPERIAL)
The Hamlyn Centre
Robotic Fast Prototyping Platform
![]()
Robotic support/performance measurement
Instituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT)
iCub Facility
Robotic support/performance measurement
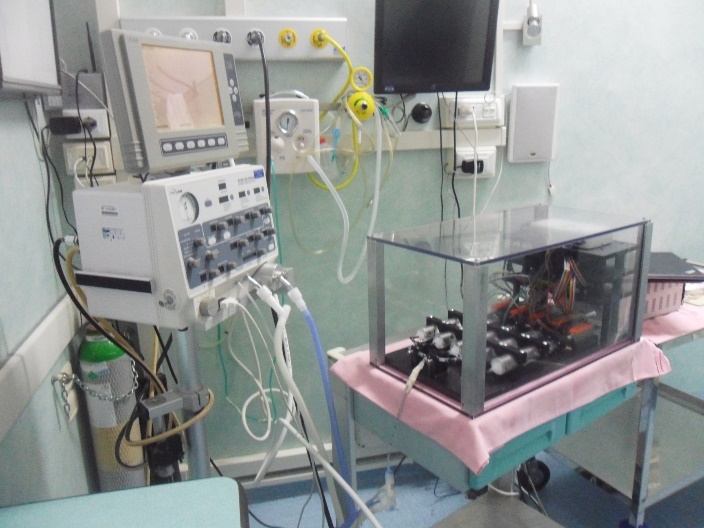
Robotic systems for high-fidelity neonatal simulation: training for medical doctors
School of Advanced Studies Sant’Anna (SSSA)
The BioRobotics Institute
Robotic systems for high-fidelity neonatal simulation: training for medical doctors
The prototype has 5 compartments arranged to reproduce anatomical distribution. Each compartment is characterized by its own adjustable compliance, and right and left respiratory branches are subjected to an independent and adjustable resistance level. The simulator is designed so as to be compatible with mechanical ventilators commonly used in NICUs, showing active behavior.
With the final aim to provide medical doctors with mechatronic and robotic systems able to answer specific and different training needs, custom training kit can be designed and realized as described above, but by following the specific clinical requirements. In this case, an extra time should be devoted to the customization of the training devices.
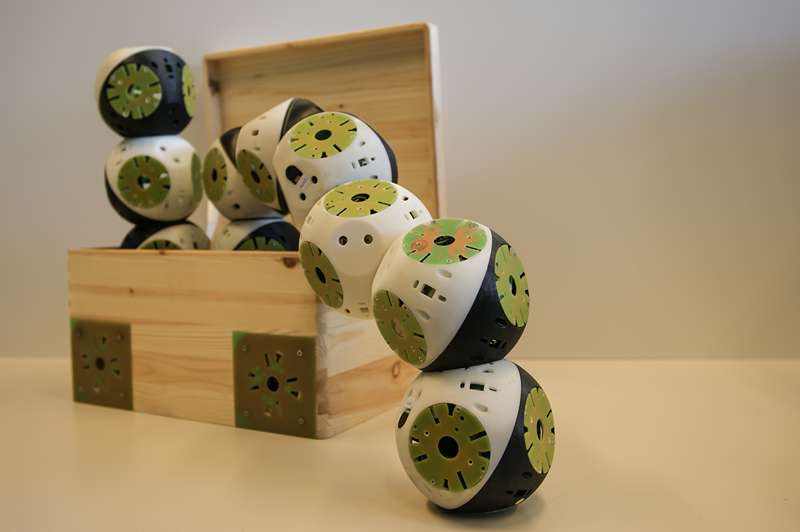

Roombots
École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL)
BioRobotics Lab
Roombots
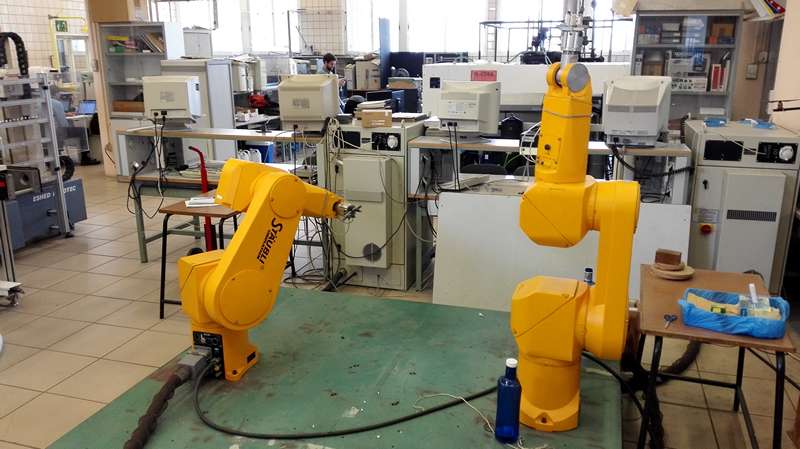

RX-90
Universidad de Sevilla (USE)
Robotics, Vision and Control Group
RX-90
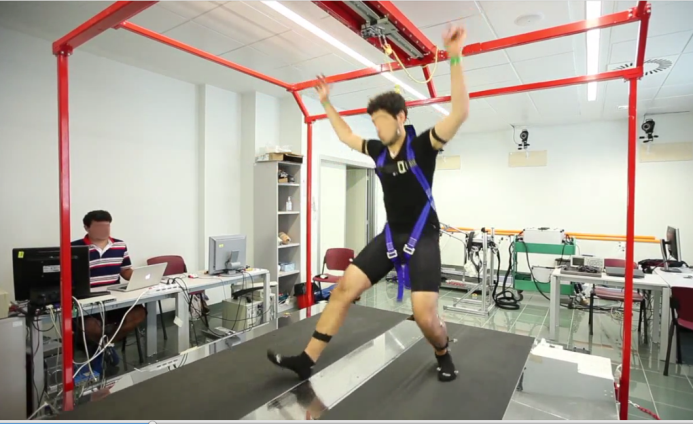

SENLY
School of Advanced Studies Sant’Anna (SSSA)
The BioRobotics Institute
SENLY
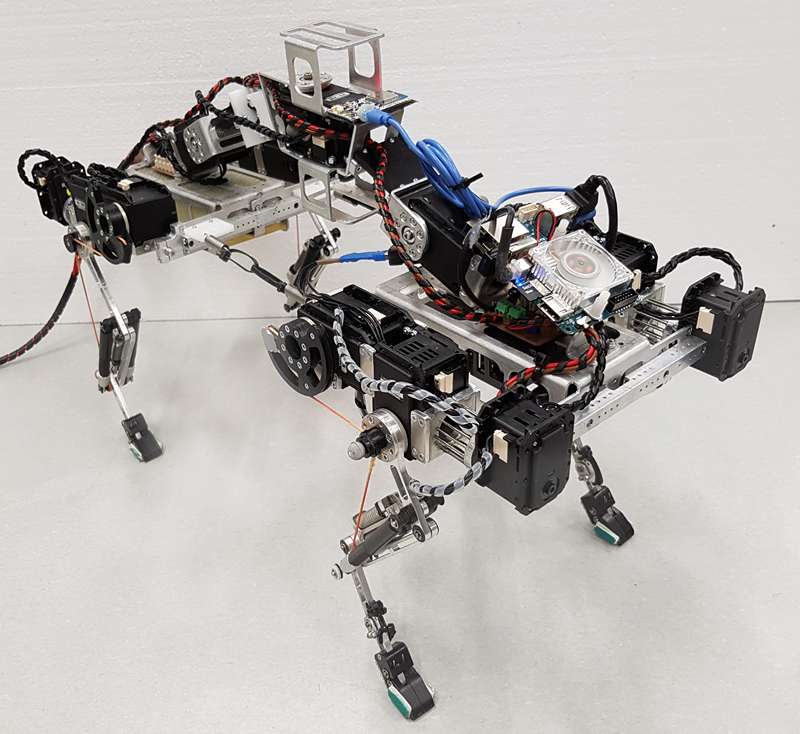
Serval
École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL)
BioRobotics Lab
Serval

SILVER (Seabed-Interaction Legged Vehicle for Exploration and Research)
School of Advanced Studies Sant’Anna (SSSA)
The BioRobotics Institute
SILVER (Seabed-Interaction Legged Vehicle for Exploration and Research)
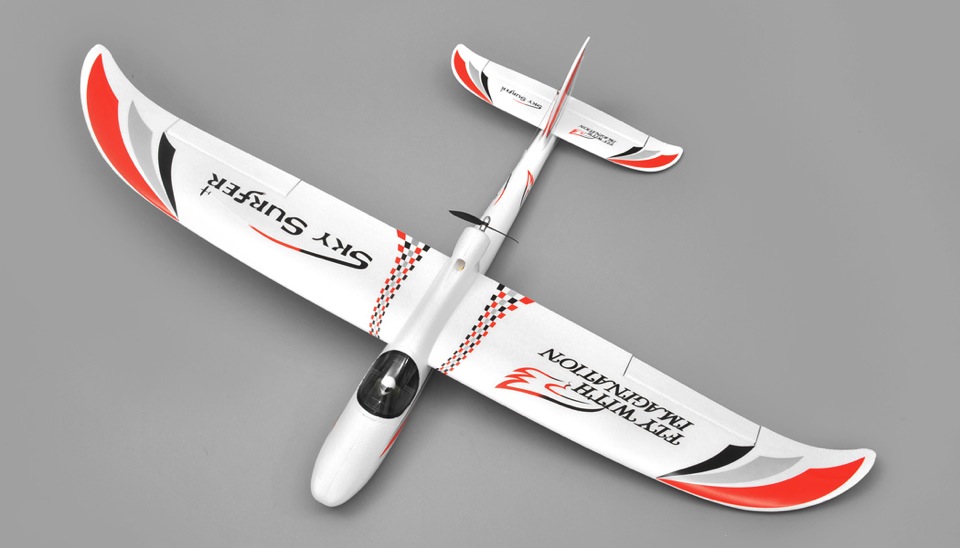

Skysurfer
Universidad de Sevilla (USE)
Robotics, Vision and Control Group
Skysurfer

Smart Experience Laboratory-SmartXP
University of Twente (UT)
Department of Robotics
Smart Experience Laboratory-SmartXP

SoftBank Robotics NAO
University of the West of England (UWE Bristol)
Bristol Robotics Laboratory
SoftBank Robotics NAO

Space53
University of Twente (UT)
Department of Robotics
Space53

STIFF-FLOP soft manipulator
School of Advanced Studies Sant’Anna (SSSA)
The BioRobotics Institute
STIFF-FLOP soft manipulator

Swimming Pool and Flow tank
École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL)
BioRobotics Lab
Swimming Pool and Flow tank

Talon
Universidad de Sevilla (USE)
Robotics, Vision and Control Group
Talon

TechMed Simulation and Training Centre
University of Twente (UT)
Department of Robotics
TechMed Simulation and Training Centre

Teo robot
Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC)
IRI
Teo robot
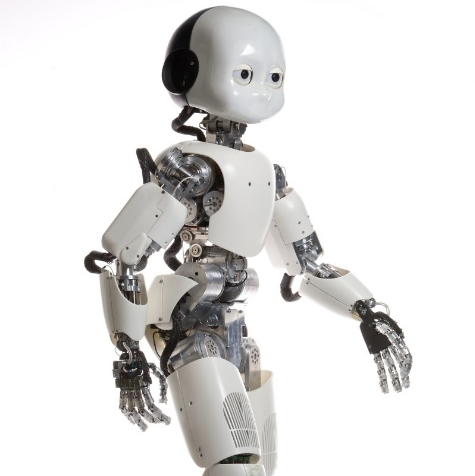

The iCub robot
Instituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT)
iCub Facility
The iCub robot
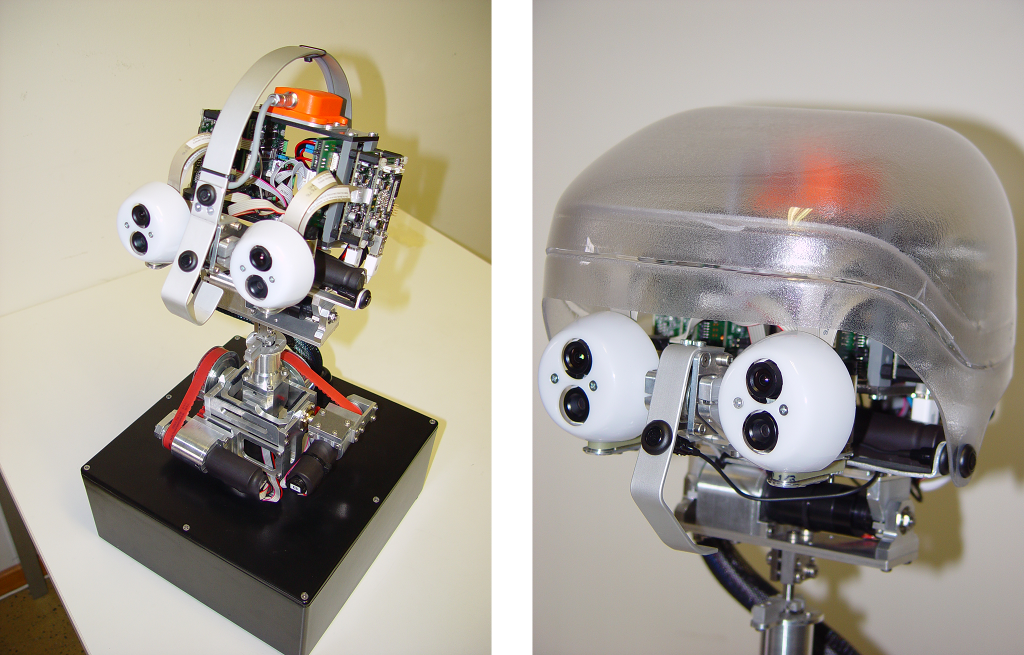
The Karlsruhe Humanoid Head
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT)
Institute of Anthropomatics and Robotics – High Performance Humanoid Technologies Lab (IAR H2T)
The Karlsruhe Humanoid Head

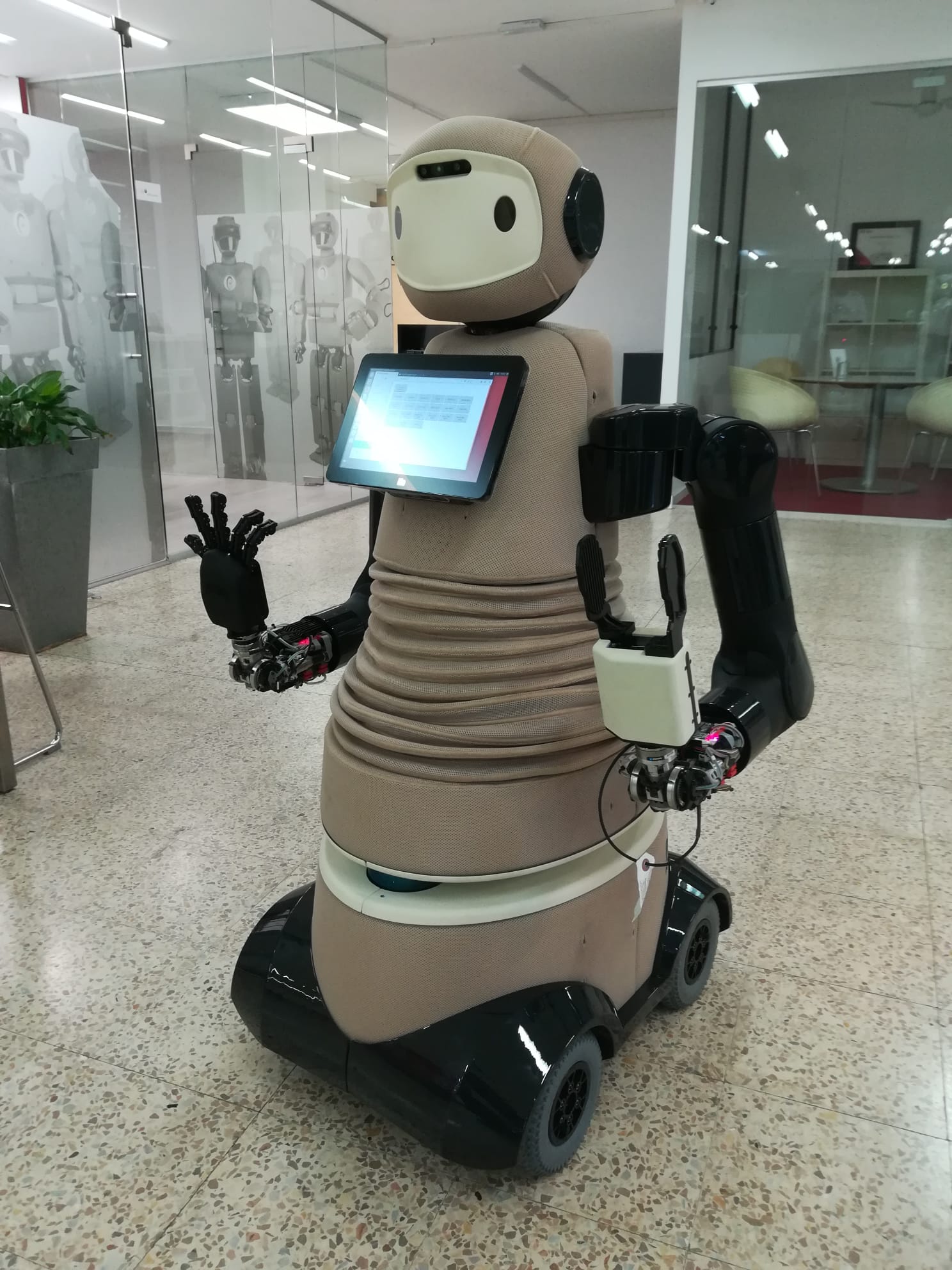
The R1 robot
Instituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT)
iCub Facility
The R1 robot

Tibi and Dabo robots
Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC)
IRI
Tibi and Dabo robots

TX90 6-axis robot
Commissariat à l’Energie Atomique (CEA)
Interactive Robotics Lab
TX90 6-axis robot

Universal Robots UR5
University of the West of England (UWE Bristol)
Robotics Innovation Facility
Universal Robots UR5
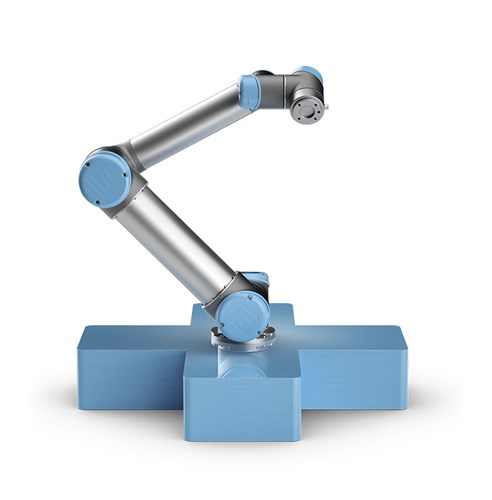
UR10 Universal Robot
Commissariat à l’Energie Atomique (CEA)
Interactive Robotics Lab
UR10 Universal Robot
![]()
Vicon Indoor Testbed
Universidad de Sevilla (USE)
Robotics, Vision and Control Group
Vicon Indoor Testbed

“Birdly” flight simulator with haptic feedback
École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL)
Laboratory of Intelligent Systems
“Birdly” flight simulator with haptic feedback


This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 730994
Dissemination

Training
Dissemination
Copyright by TERRINet. All rights reserved. – Designed by RGR